Other Common Names:
Polyurea Classification: Two-component (Spray Type, Brush Type) / One-component (Brush Type)

Features
Limitations



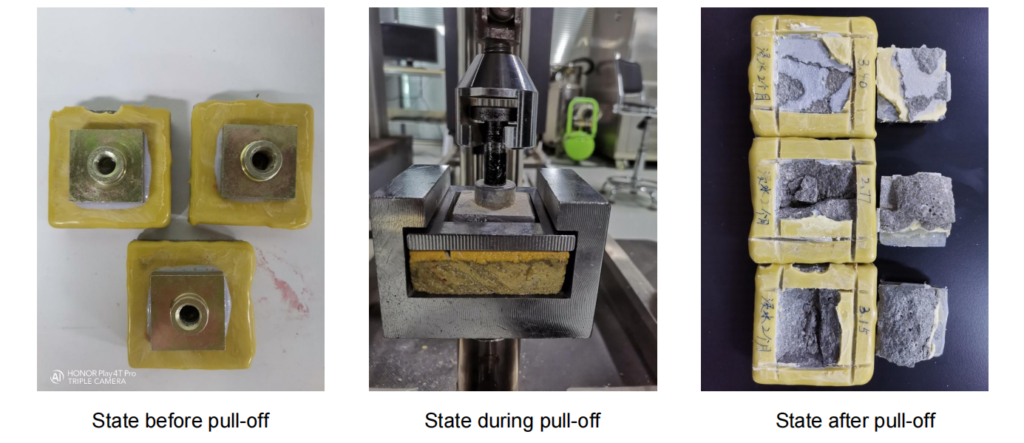
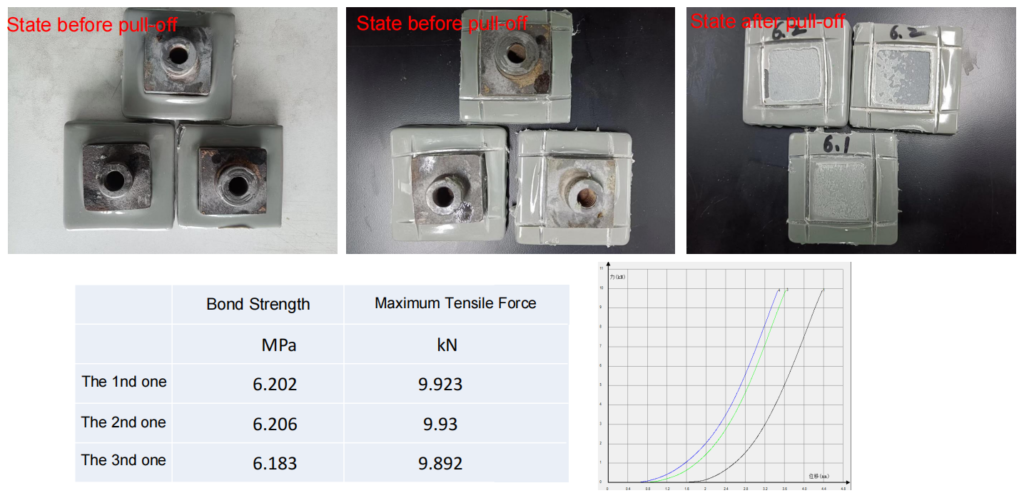

Note: Data measured by the pull-off method (vertical pull-off test) can be misleading. Even with poor adhesion, qualified values can still be obtained, for example, if the cutting around the pull-off dolly is incomplete.
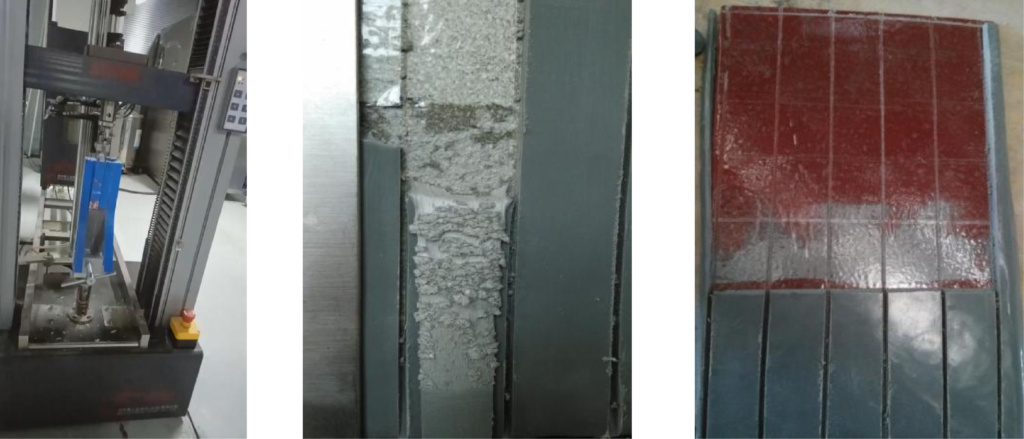

A pair of pliers can be used on-site to simulate the peeling test by tearing
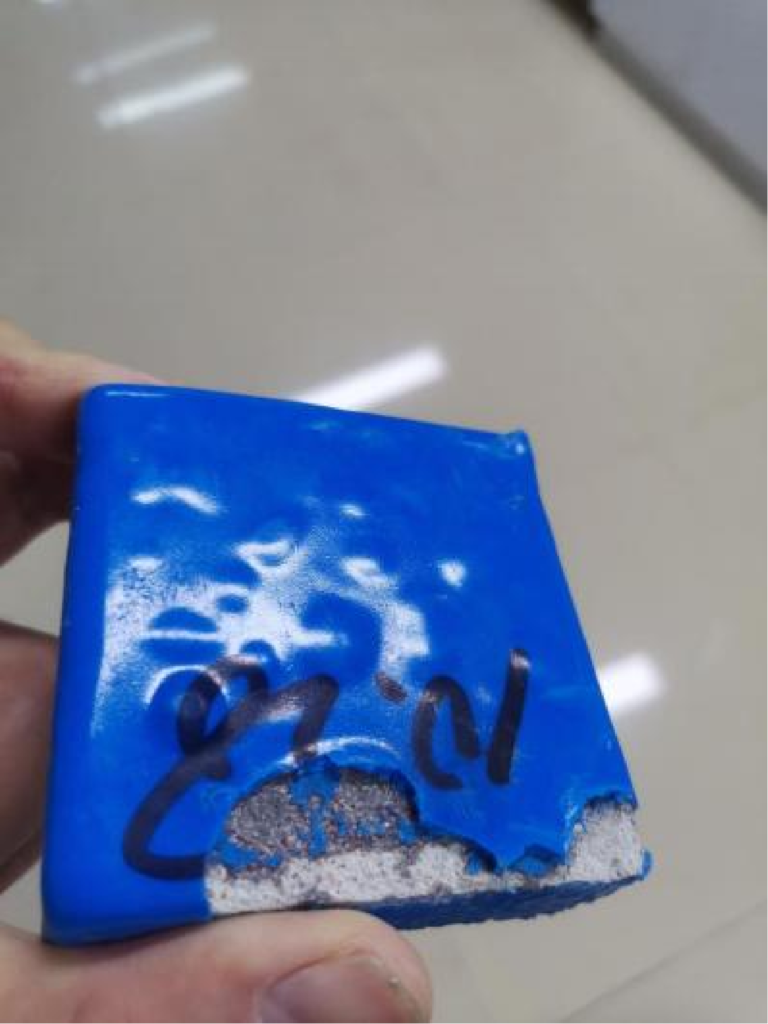


Low-temperature flexibility at -40℃
High-temperature water immersion at 70℃: Blistering
Upper limit temperature for liquid media: 60℃
Chemical Medium Resistance (23℃ / 1 year)
| Medium names | Soaking results | Medium Names | Soaking results |
| 10% acetic acid | Very good | Seawater | Very good |
| 10% hydrochloric acid | Very good | Xylene | Not recommended |
| 30% sulfuric acid | Very good | Crude Oil | Very good |
| 10% phosphoric acid | Good color change | Gasoline | Not recommended |
| 20% ammonia water | Very good | Diesel | Very good |
| 20% potassium hydroxide | Good color change | Engine Oil | Very good |
| 50% sodium hydroxide | Very good | Hydraulic Oil | Very good |
| Saturated brine | Very good | Ammonium Nitrate | Very good |

| Serial Number | Tensile strength (MPa) | Elongation at break (%) |
| 10% Sulfuric Acid | 29.1 | 466.5 |
| 20% Sulfuric Acid | 29 | 459.7 |
| 30% Sulfuric Acid | 27.7 | 448.6 |
| 50% Sodium Hydroxide | 29.9 | 463.6 |
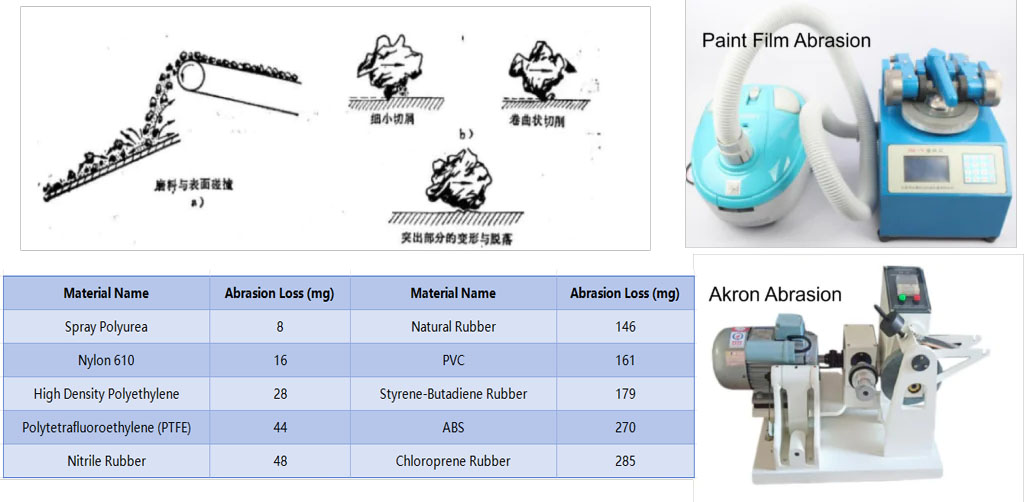
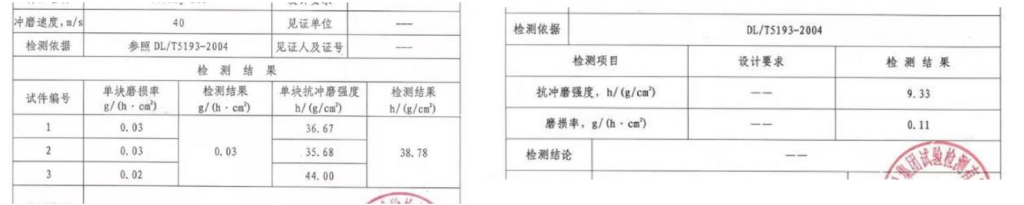
Erosion Resistance of Two-component Spray Polyurea
Erosion Resistance of One-component Polyurea
| Material Types | Weight loss g | Wear rate (g/cm²·h) | Wear volume (cm³) | Surface Condition |
| Abrasion-resistant polyurea elastomer | 2.5 | 0.027 | 2.45 | The coating surface remained largely unchanged, with no visible grooves. |
| Secondary aggregate concrete with limestone f28 = 66.5 MPa | 414 | 0.44 | 159.2 | The inner wall of the specimen showed numerous grooves and other defects after grinding. |
| Secondary aggregate concrete with granite f28 = 65.6 MPa | 98 | 0.104 | 37.7 | The inner wall of the specimen showed numerous grooves and other defects after grinding. |



GB/T 23446-2009
Spray Polyurea Waterproof Coating
JC/T 2252-2014
Primers and Putties for Spray Polyurea
HG/T 3831-2006
Spray Polyurea Protective Materials
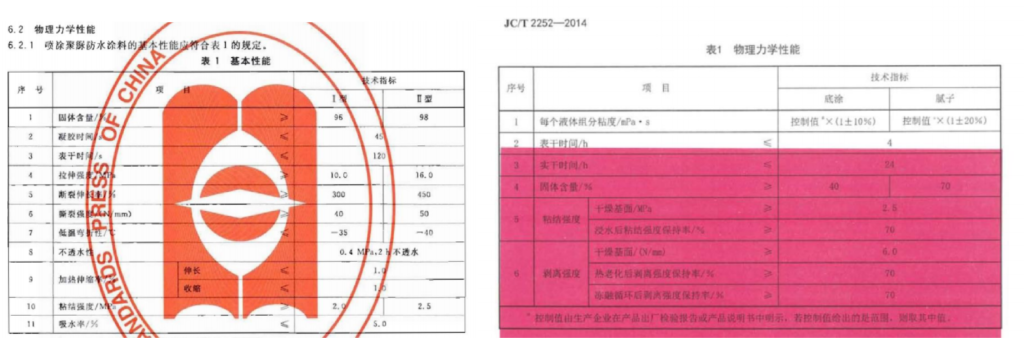
GB/T 23446-2009
The Most Important Standard for Material Properties
JC/T 2252-2014
Loss of Adhesion
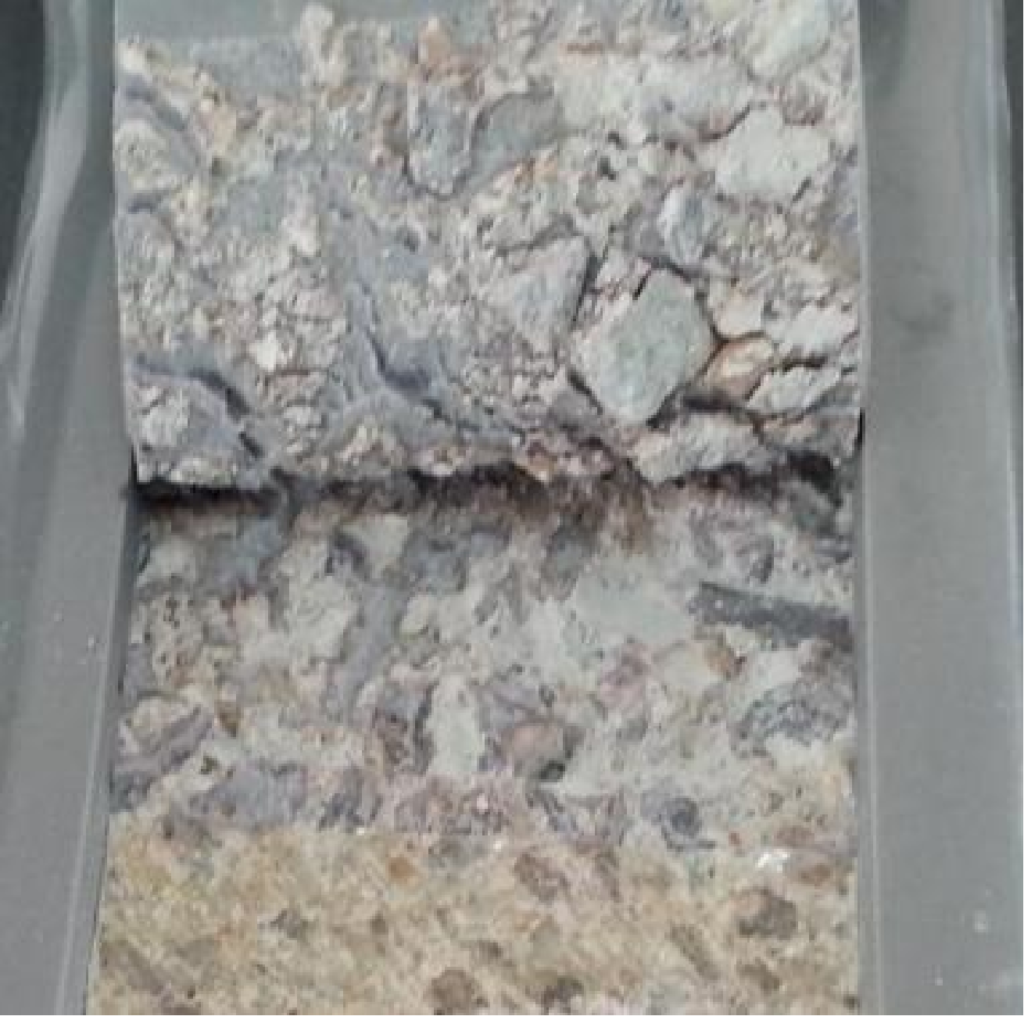
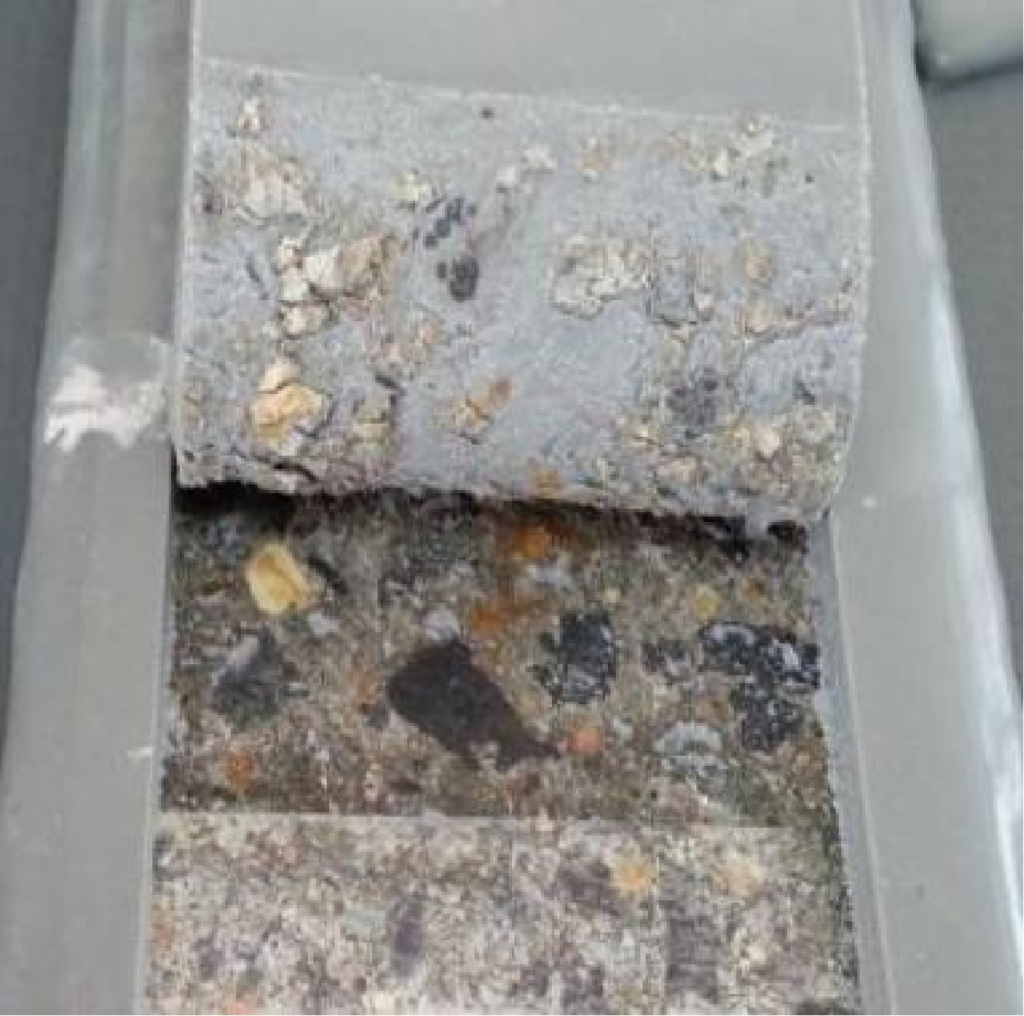



Routine
Immersion Damage
Freeze-Thaw Damage
Plasticization effect of water and damage to adhesive hydrogen bonds (chemical bonds)
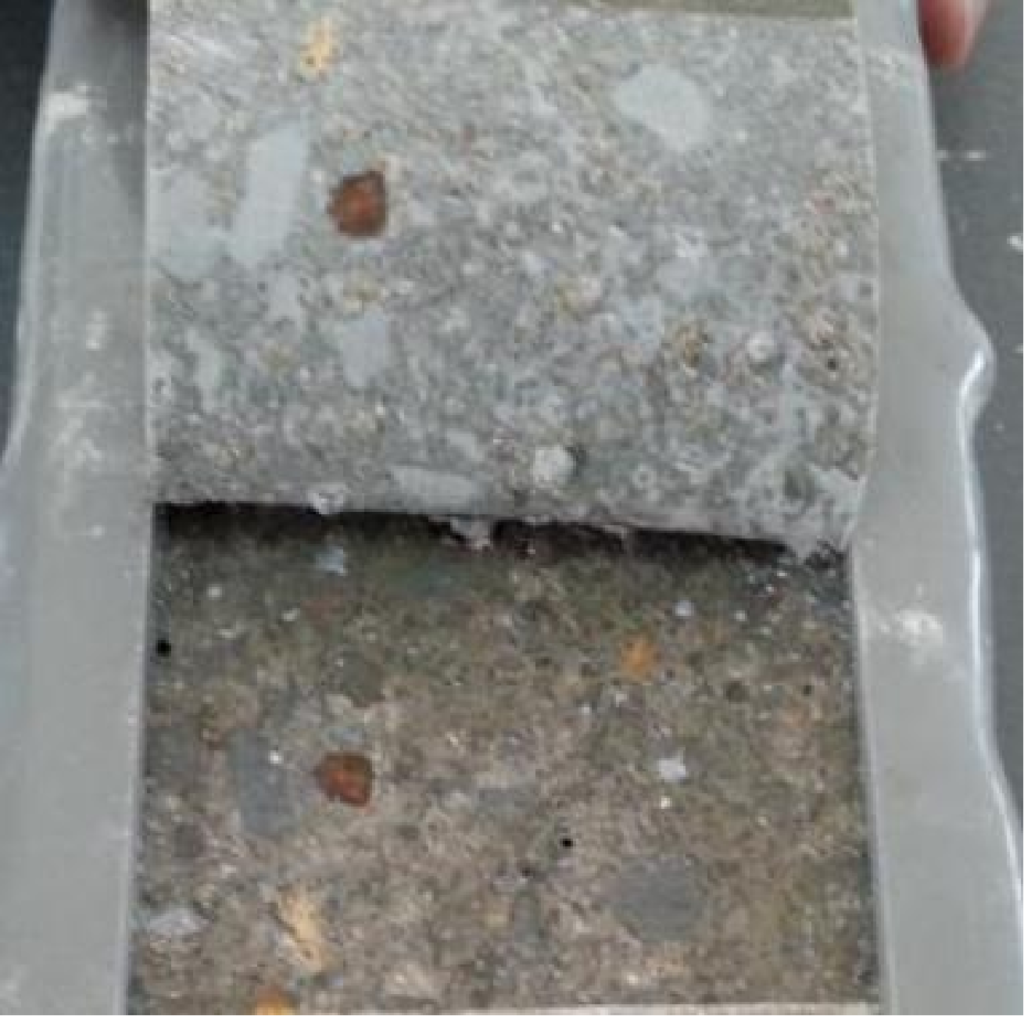
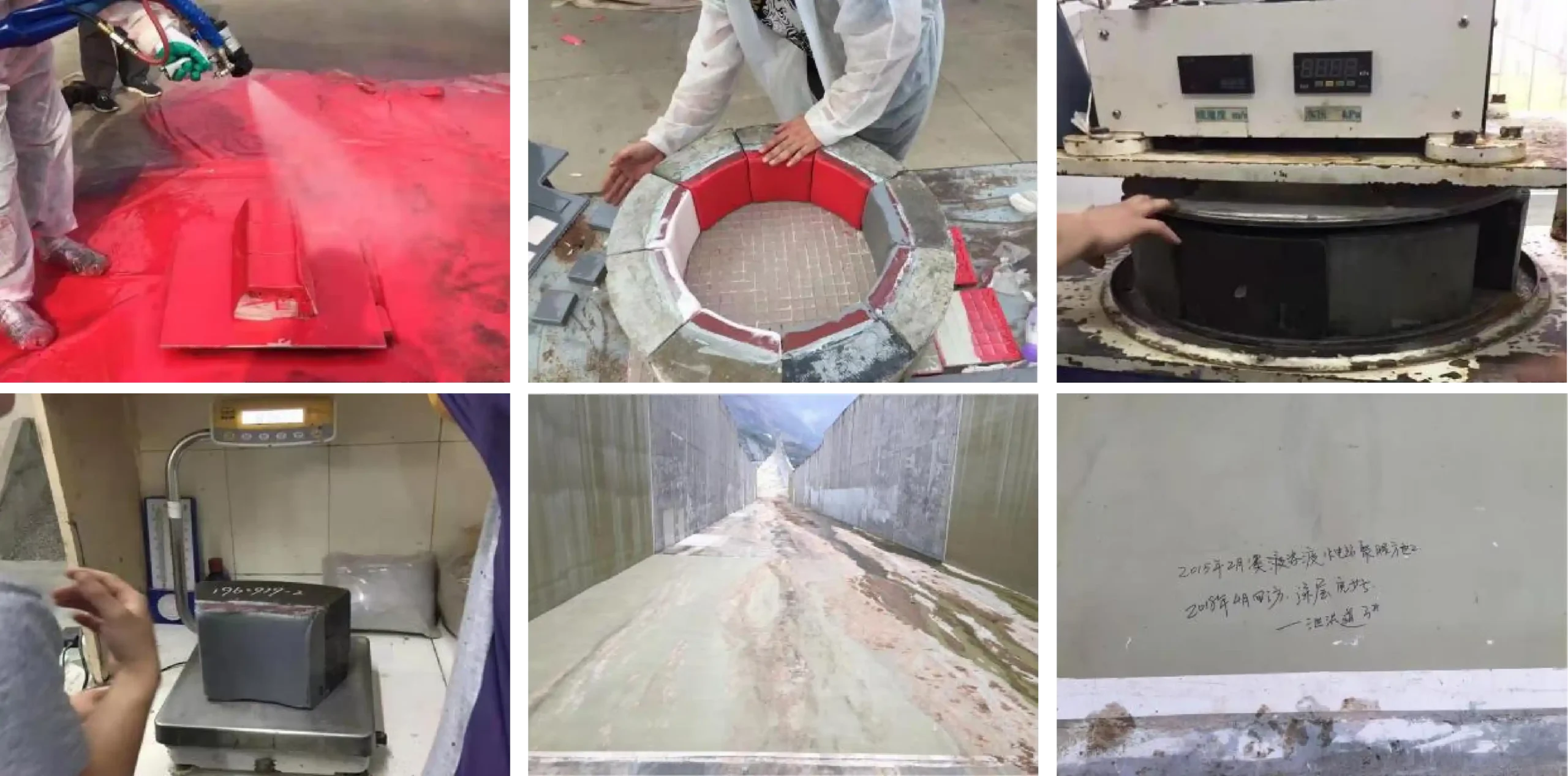
Persistence of Adhesion Under Long-term Immersion
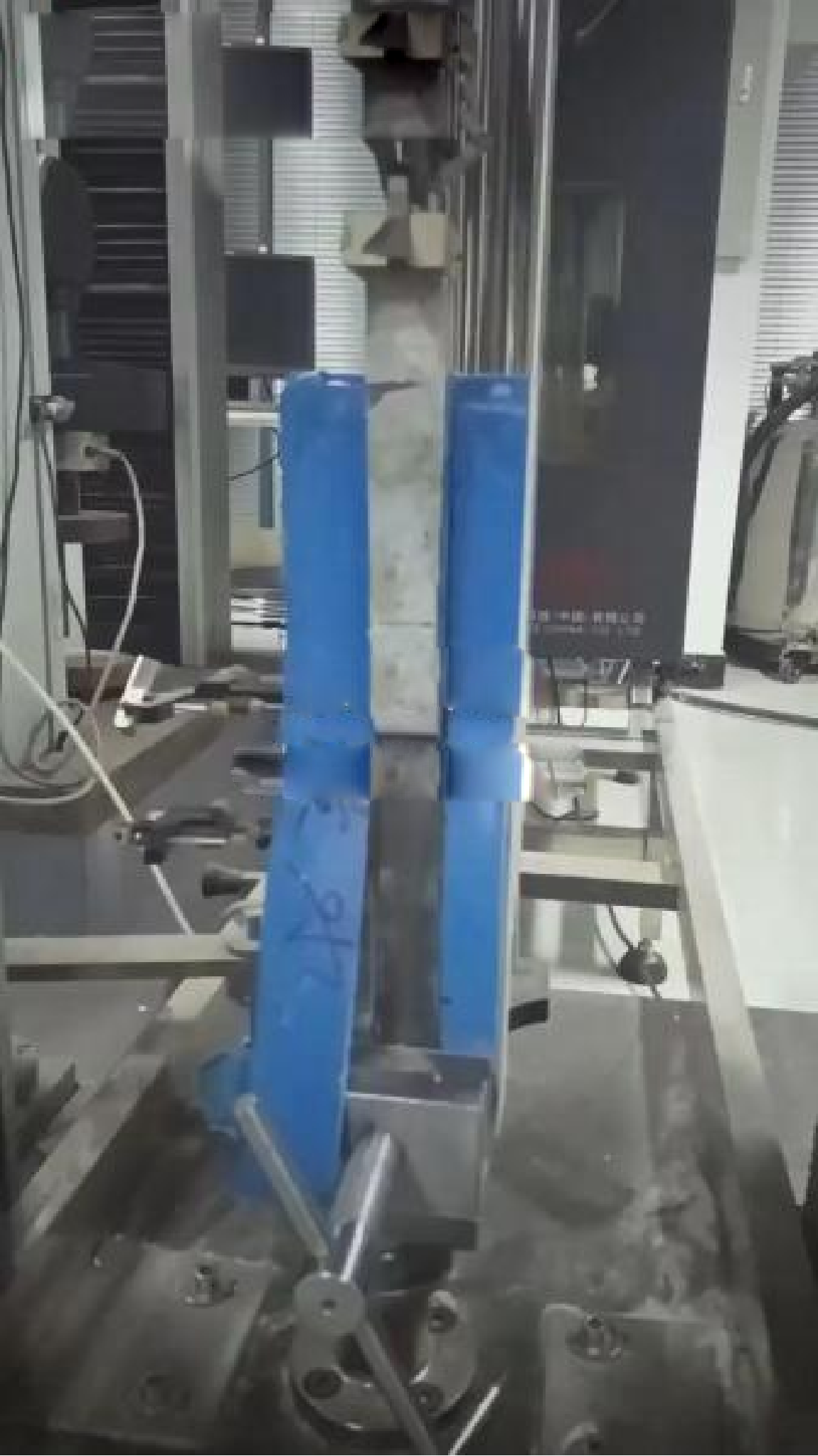


180° Peel Test After 3 Months of Immersion
1 Year of Immersion






















| Differences in corrosion rates of different surface treatment coatings | ||
| Serial Number | Treatment methods | Rust and corrosion status of the coating |
| 1 | No rust removal | 60% |
| 2 | Manual rust removal | 20% |
| 3 | Acid pickling | 15% |
| 4 | Sandblasting | Only a few rust spots |
| Coating damage period | ||
| Serial Number | Treatment methods | Repainting deadline/year |
| 1 | Air blowing, wire brush cleaning | 3 |
| 2 | Flame purification | 5 |
| 3 | Acid pickling, phosphoric acid impregnation | 5.5 |
| 4 | Sandblasting or shot blasting | 7 |
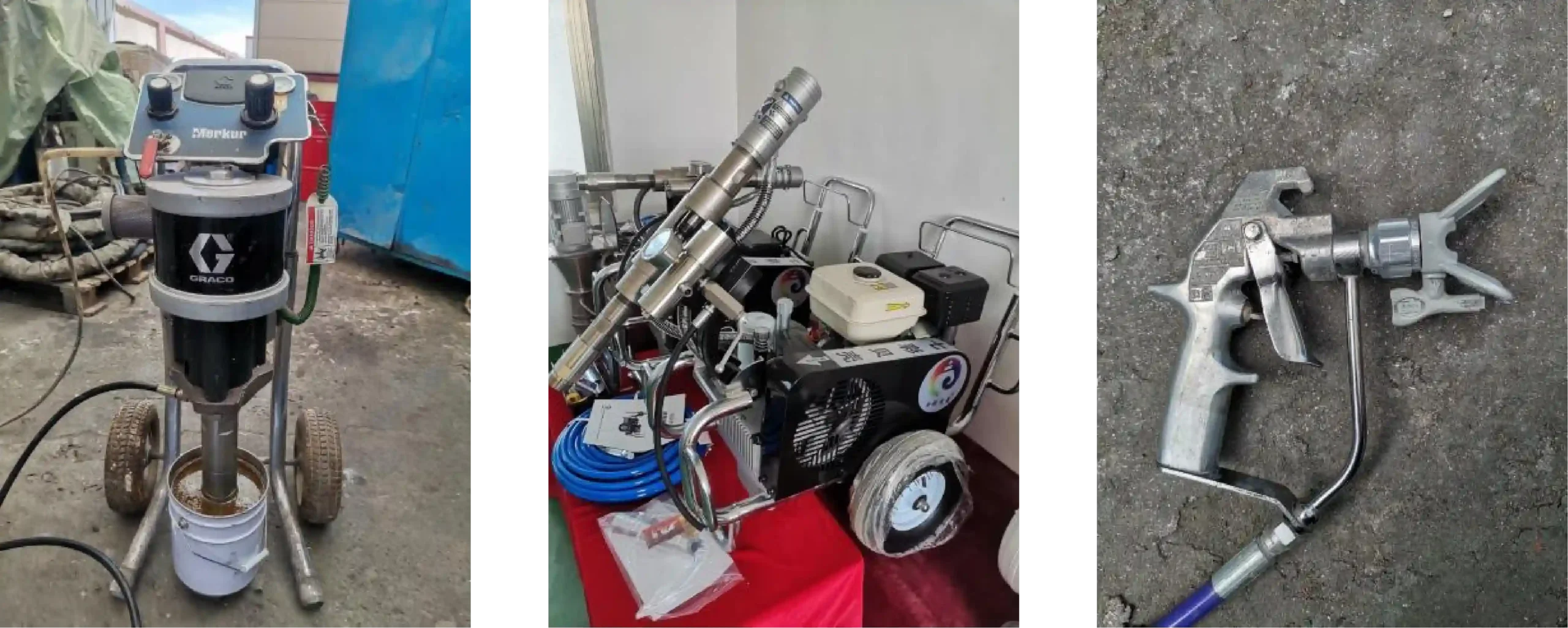

Pneumatic pumps are suitable for low-viscosity or solvent-based spraying.
Hydraulic pumps are suitable for high-viscosity or solvent-free spraying.
spray gun
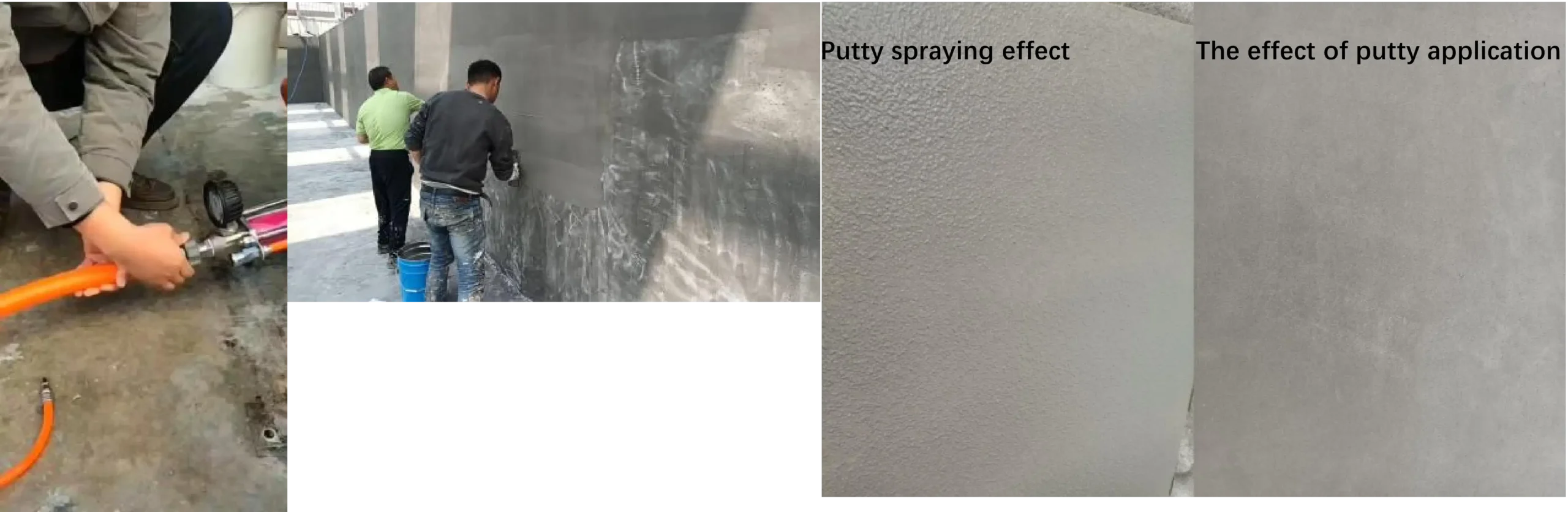



Recommendation: Use equipment spraying as the primary method, supplemented by manual scraping and smoothing.
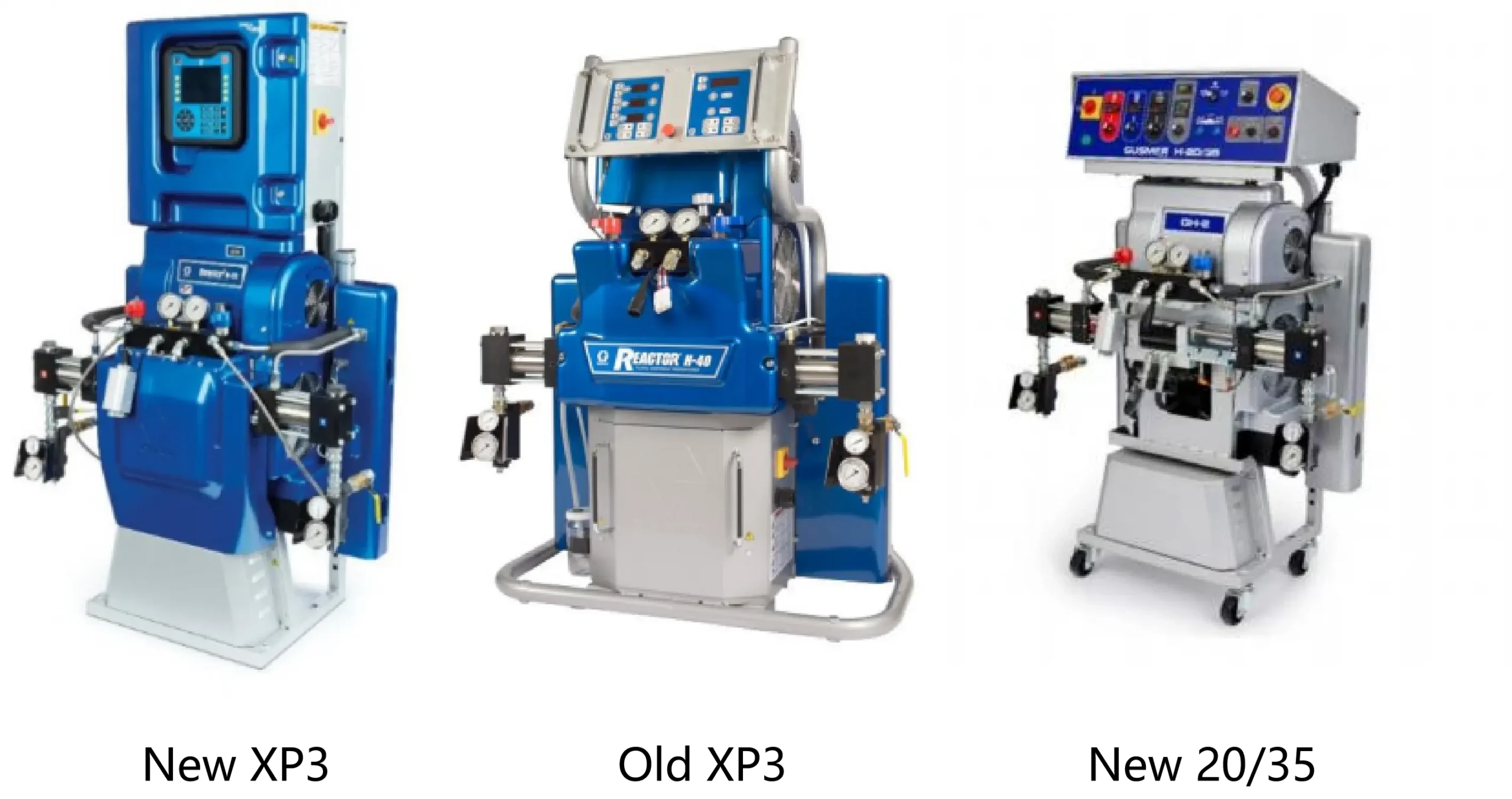
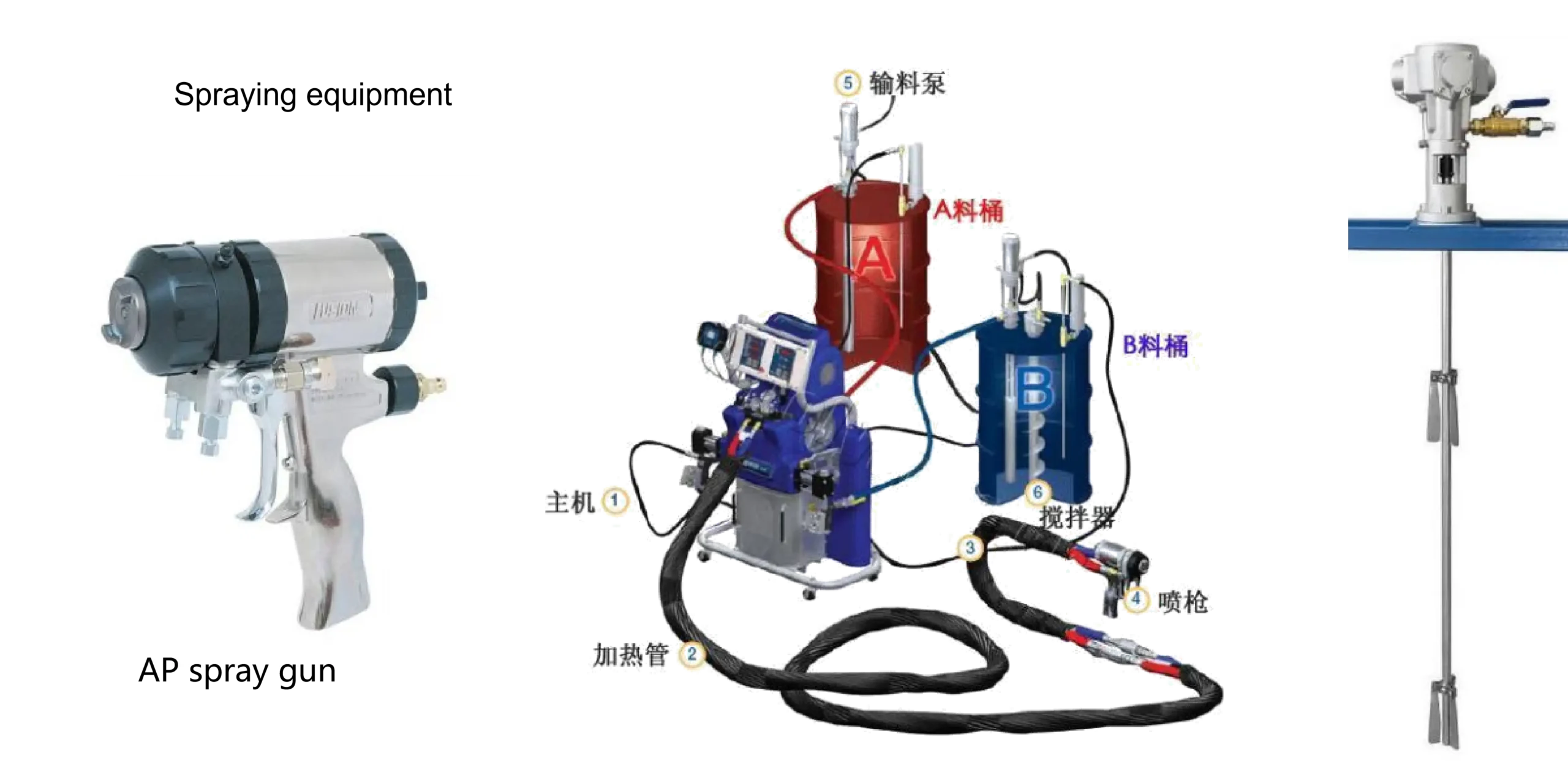

Graco H-xp3 Basic Parameters
Maximum Output Pressure: 3500 Psi (240 bar)
Maximum Output Flow Rate: 2.8 gallons/min (10.6 liters/min)
Maximum Heating Power: 20 kW
Operating Voltage: 380V
Maximum Heating Temperature: 88℃
Maximum Supported Pipe Length: 123 meters
Weight: 271 kg
During Spraying:
Component A Heating Temperature: 60-65℃
Component B Heating Temperature: 60-65℃
Pipe Heating Temperature: 60-65℃
Spraying Static Pressure: 2000-2500 Psi

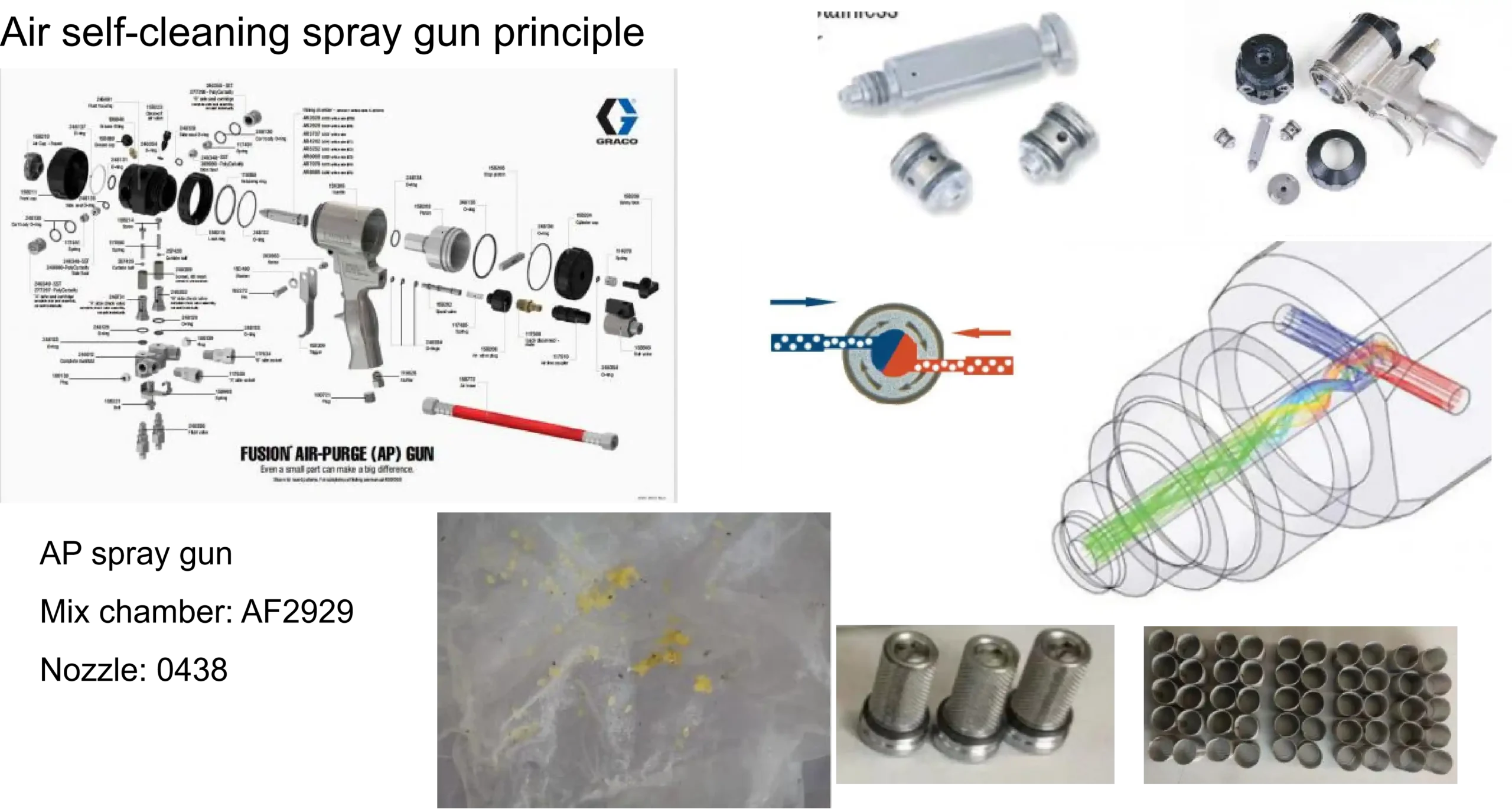
AP = Air-Purge / Air Self-Cleaning
MP = Mechanical-Purge Spray Gun / Mechanical Self-Cleaning Spray Gun

| Serial Number | Process | Tools | Personnel | Remarks |
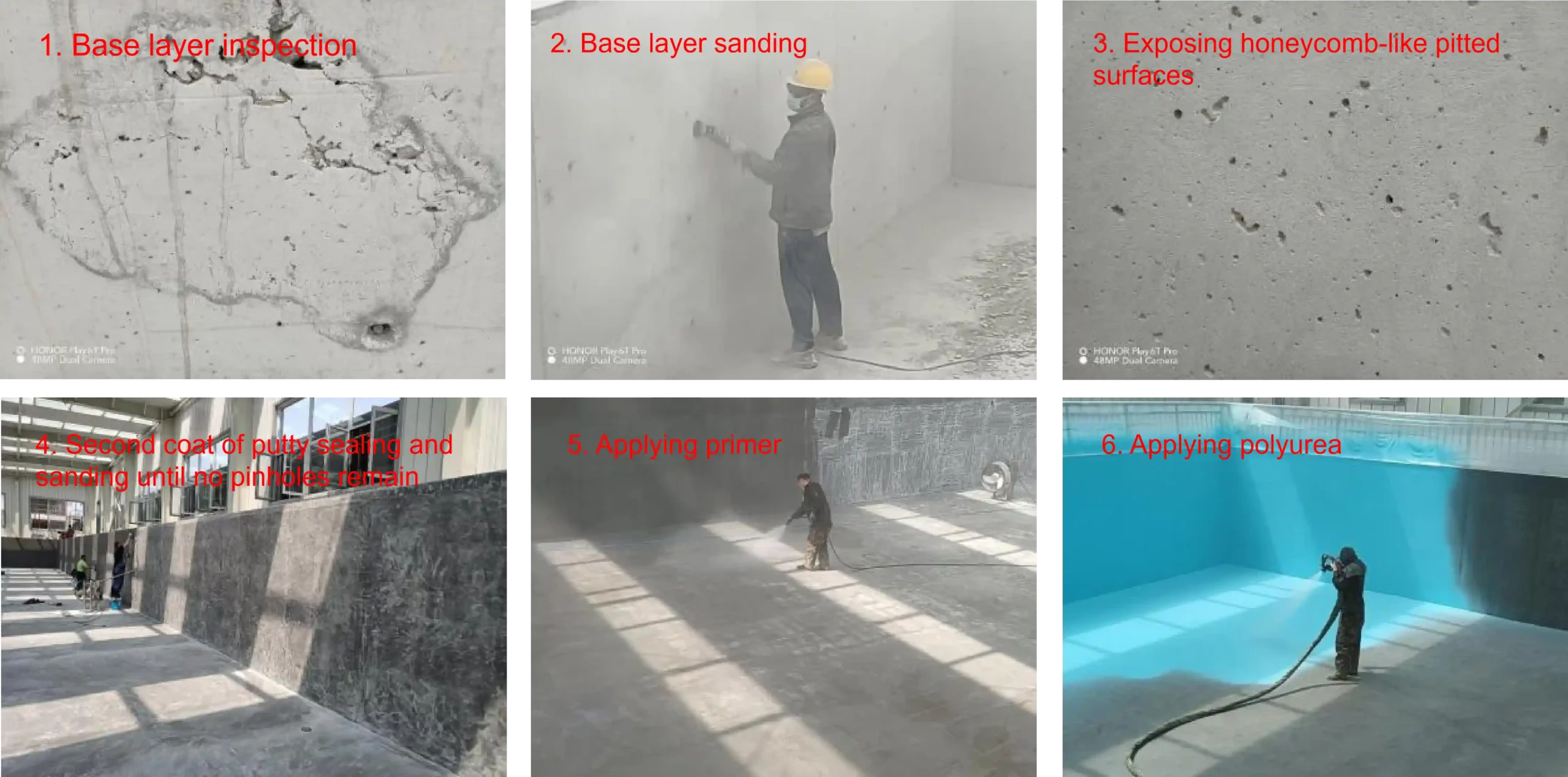
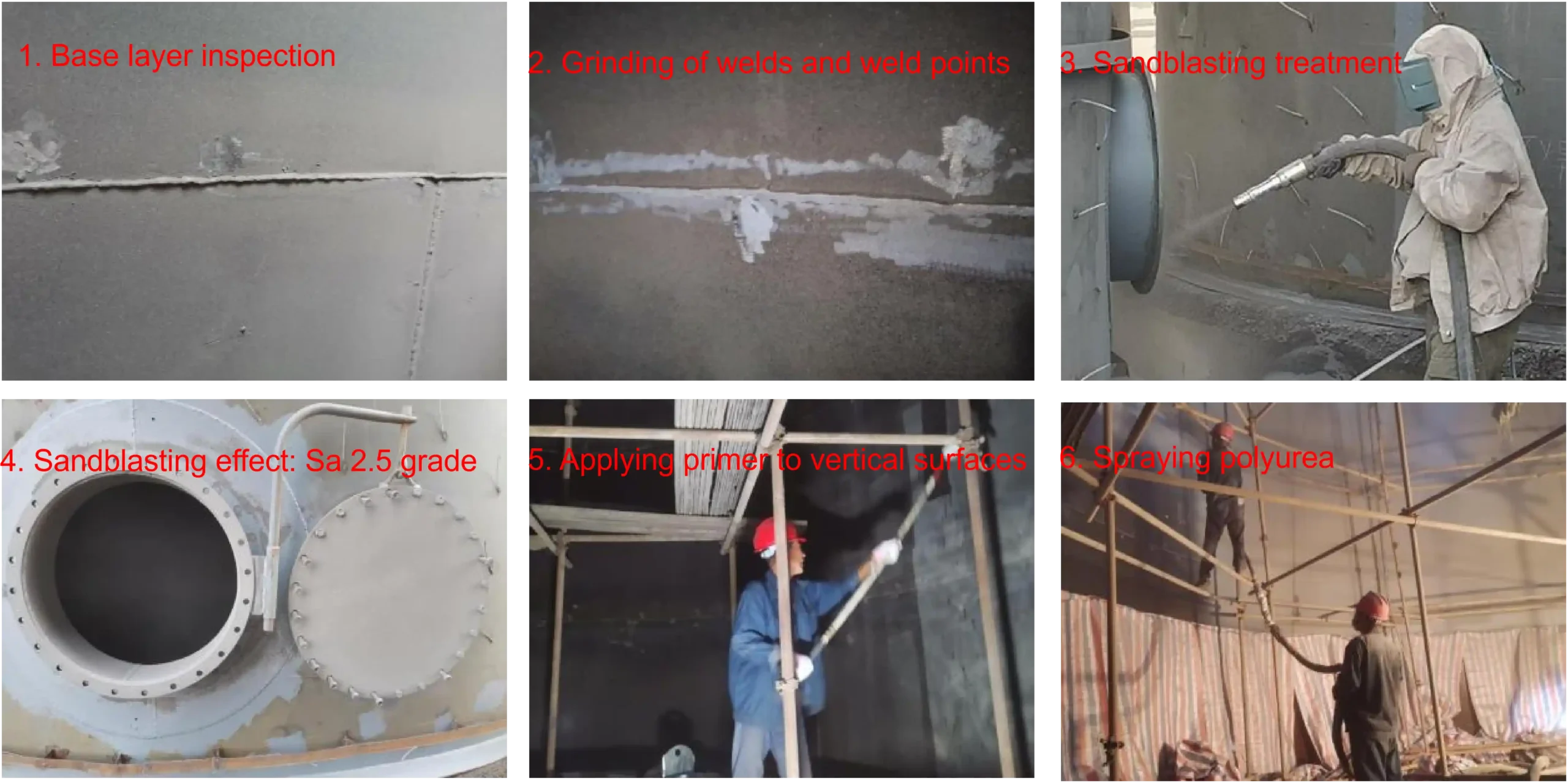
| 1 | Substrate preparation (cleaning, grinding, dust removal) | Angle grinders, floor grinders, high-pressure water guns, sandblasting machines, shot blasting machines, grooving machines, vacuum cleaners, etc. | 4-6 people | Scaffolding, suspended platforms, and elevators will be determined on a case-by-case basis. |
| 2 | Substrate sealing | Screw pump sprayers, high-pressure airless sprayers/pneumatic pump sprayers, electronic scales, handheld mixers, etc. | 4-6 people | Low-value consumables such as scrapers and rollers will be determined on a case-by-case basis. |
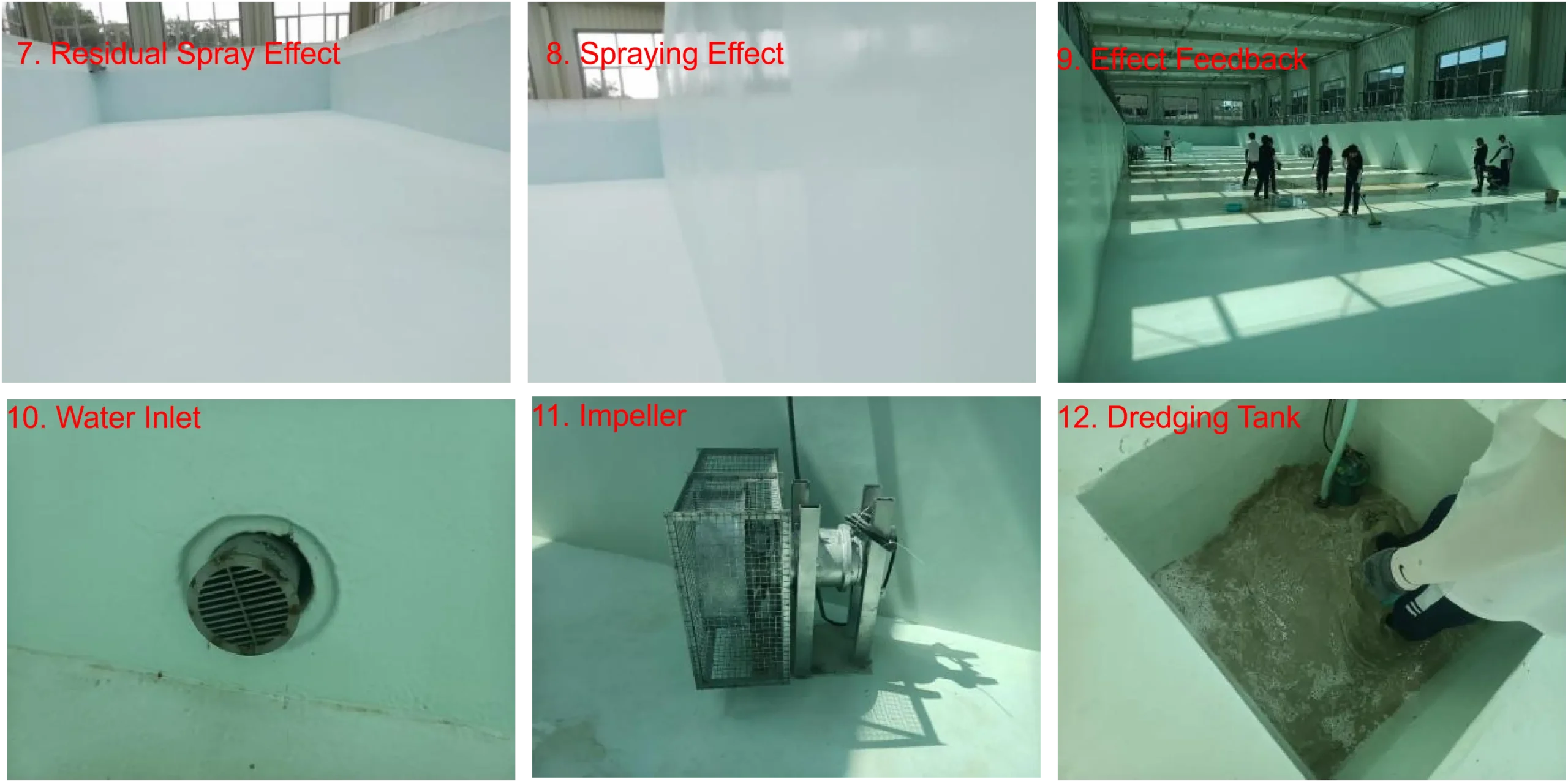
| 3 | Polyurea spraying | Polyurea sprayers, air compressors, refrigerated dryers, pneumatic mixers, etc. | 3-6 people | Protective consumables will be determined on a case-by-case basis. |
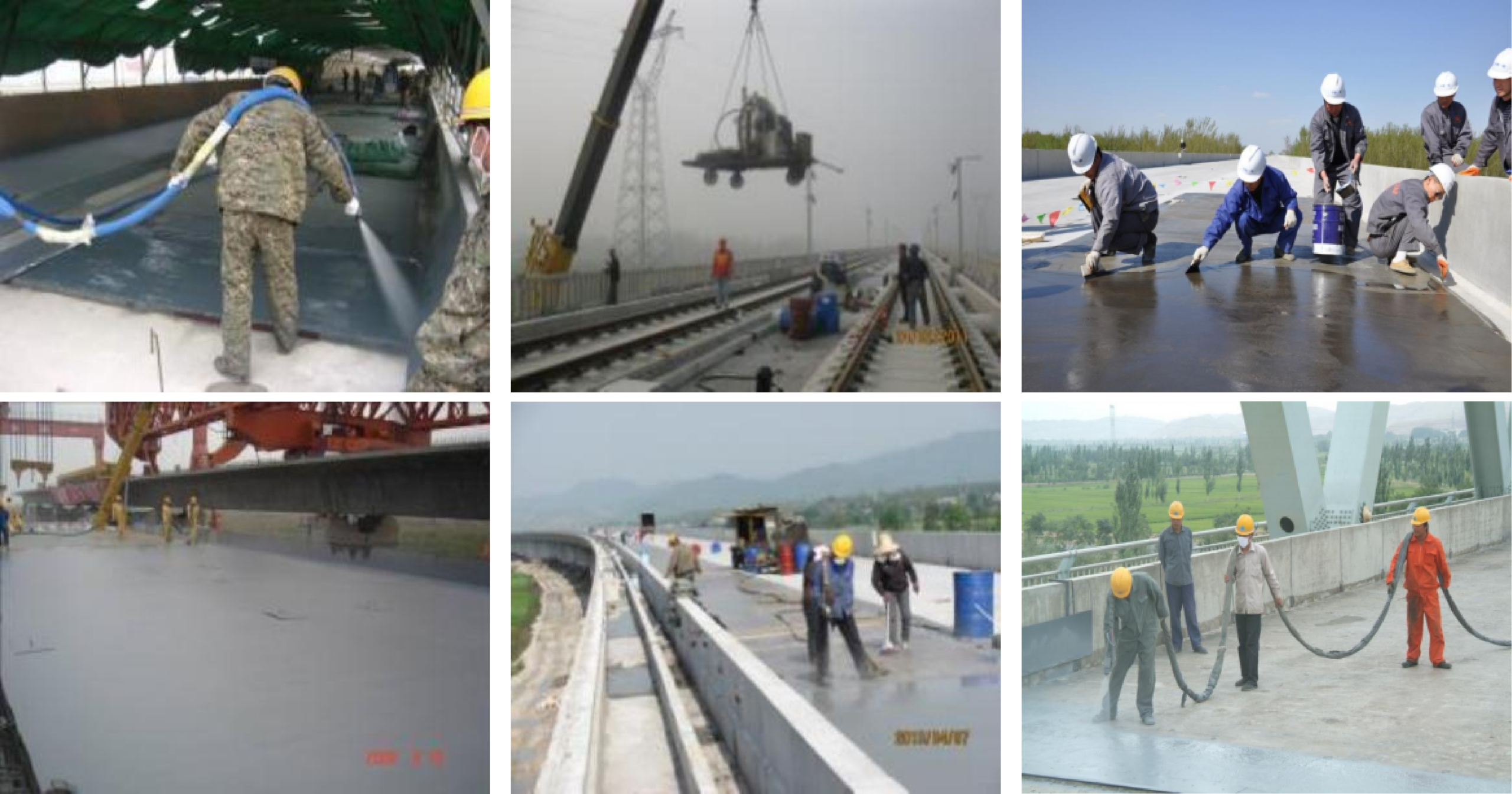
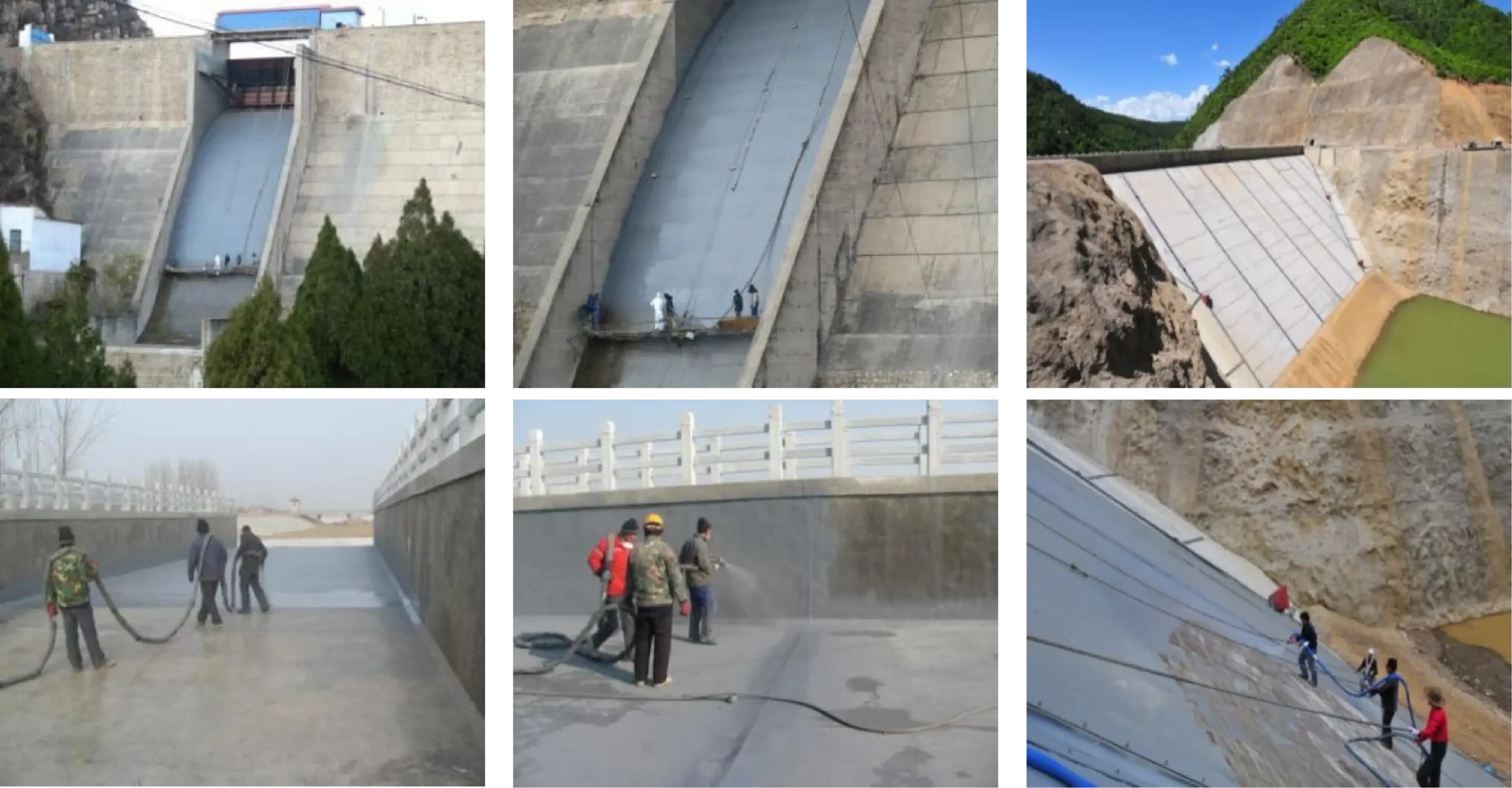
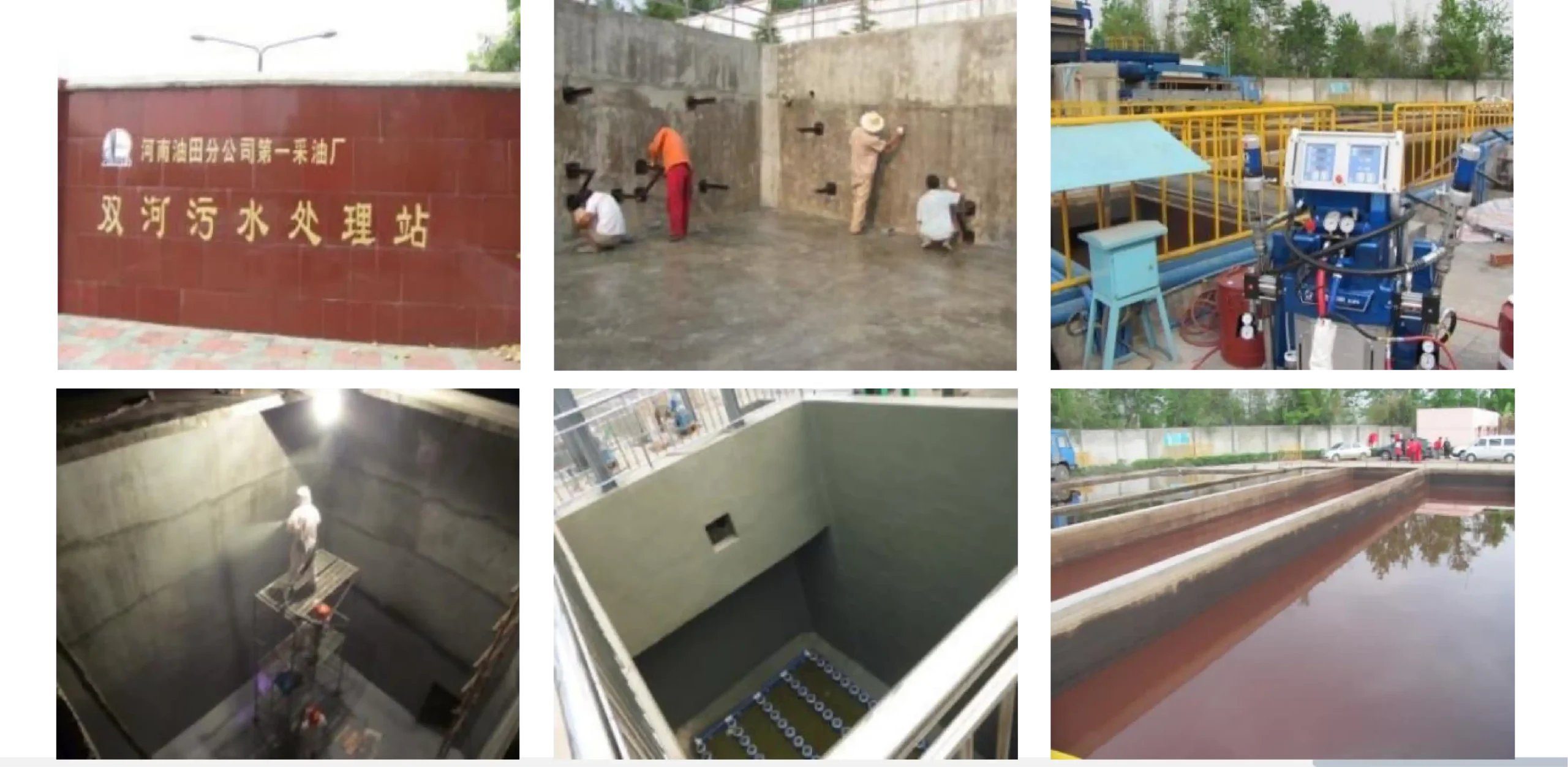
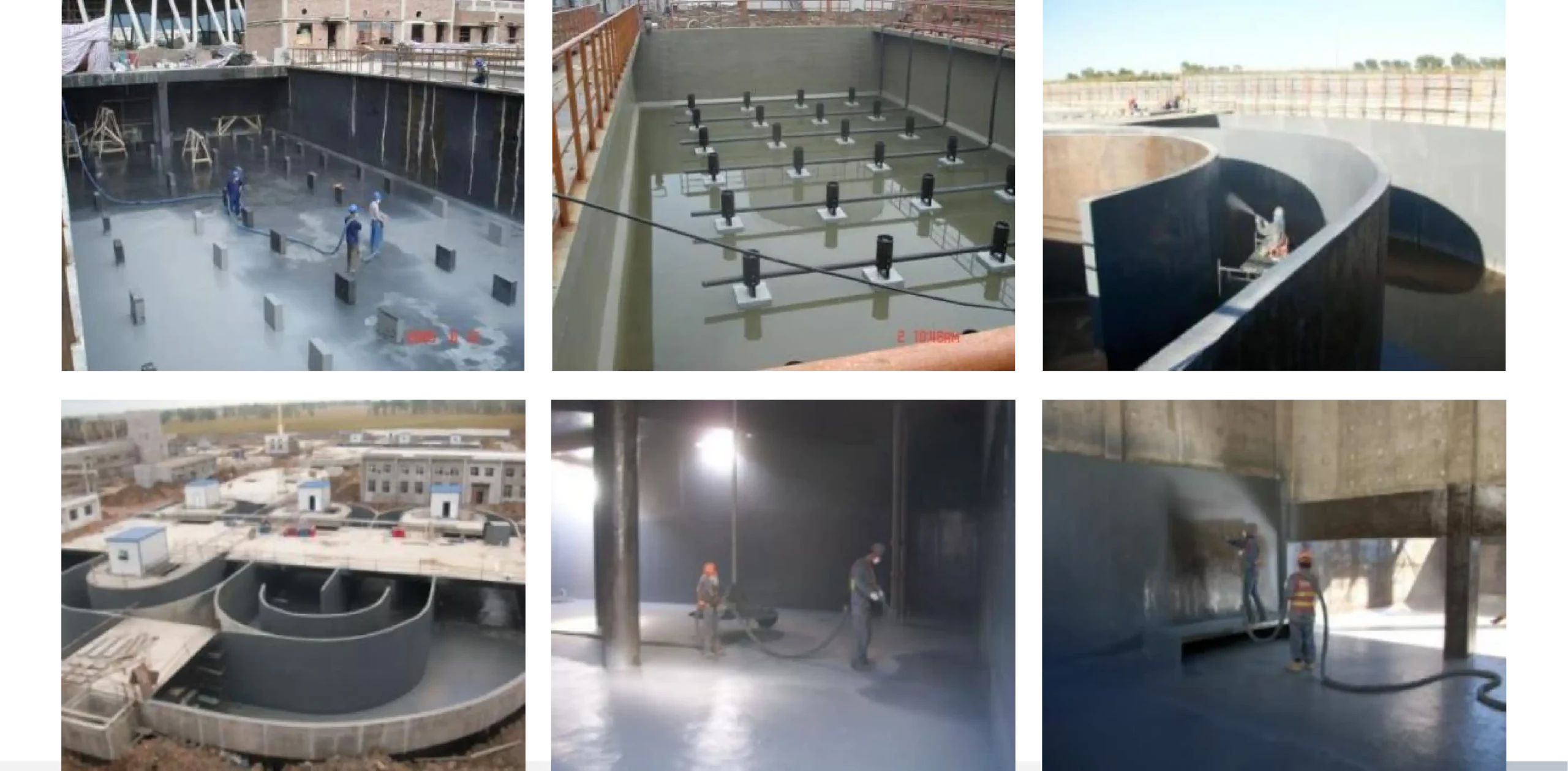
In the construction of large projects, there are specialized teams to carry out tasks such as scaffolding/suspended platform erection/dismantling, base layer grinding, base layer sealing, and polyurea spraying.

HG/T 20273-2011
Technical Specification for Coating Engineering of Spray-applied Polyurea Protective Materials
JGJ/T 200-2010
Technical Specification for Sprayed Polyurea Waterproofing Engineering
T/CECS 679-2020
Technical Specification for Polyurea Coating Application
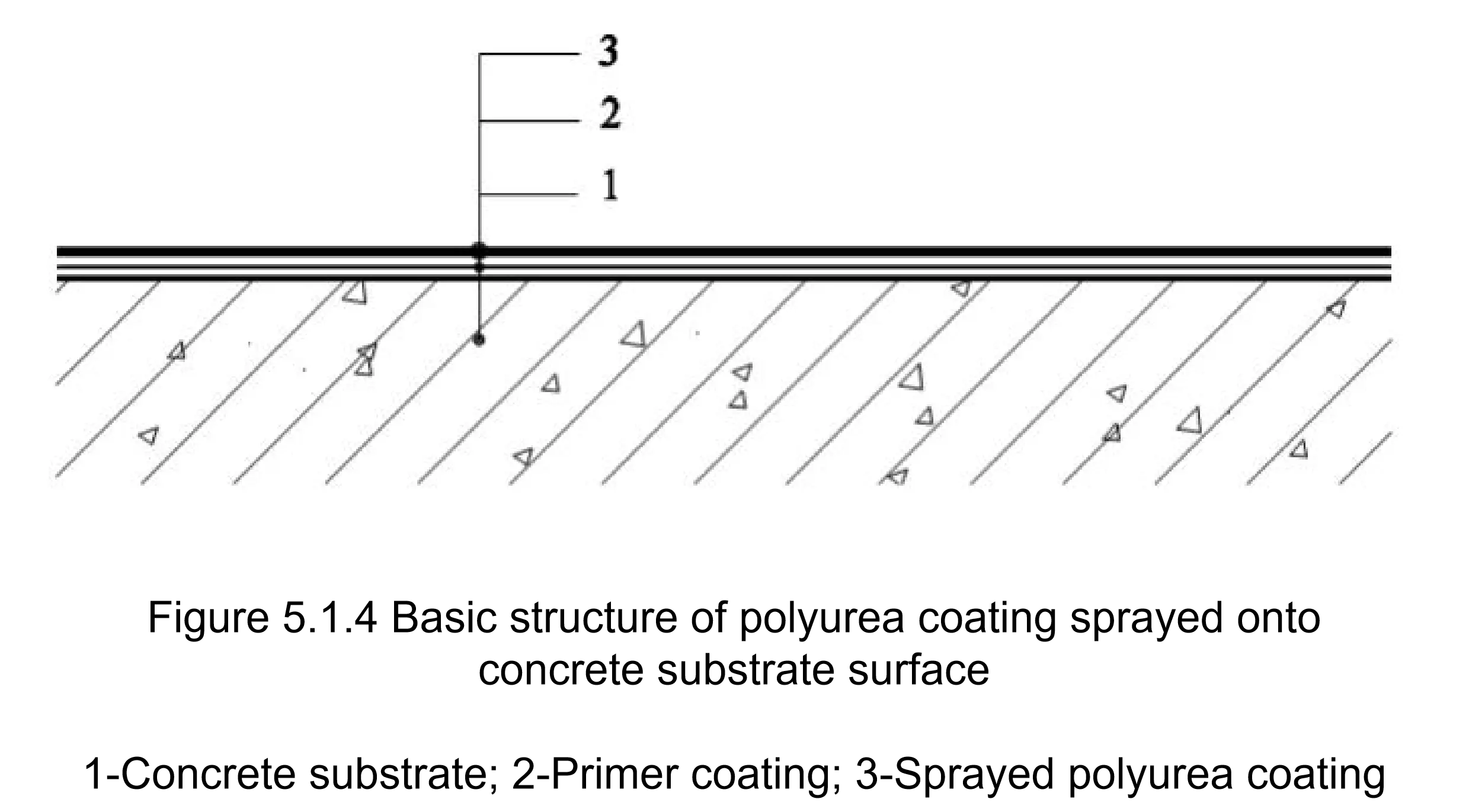

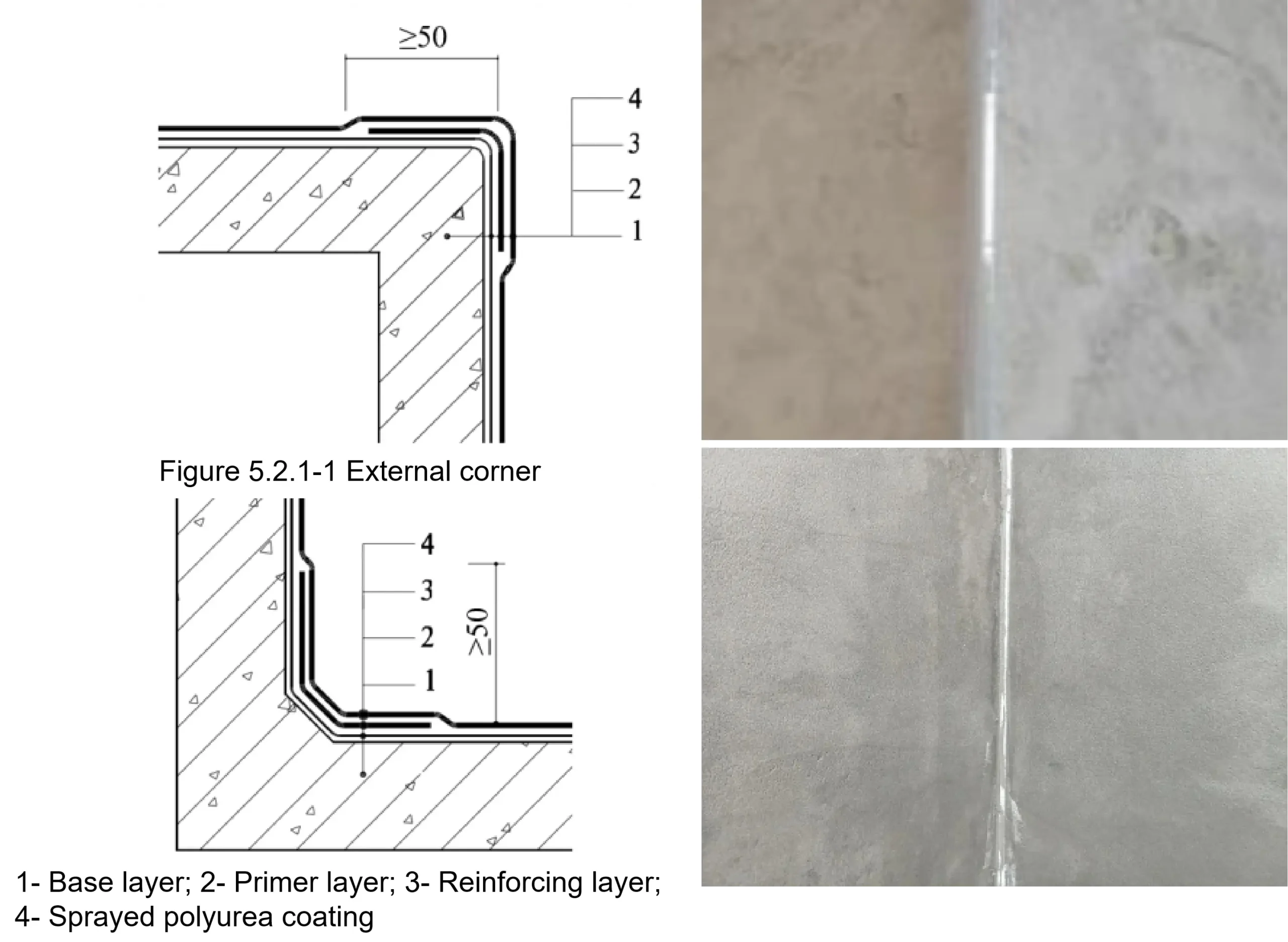
Specific application method: Grind the corners to create a rounded shape, and apply a thicker layer during spraying.
Specific application method: Use putty/mortar to create rounded corners, and apply a thicker layer during spraying.
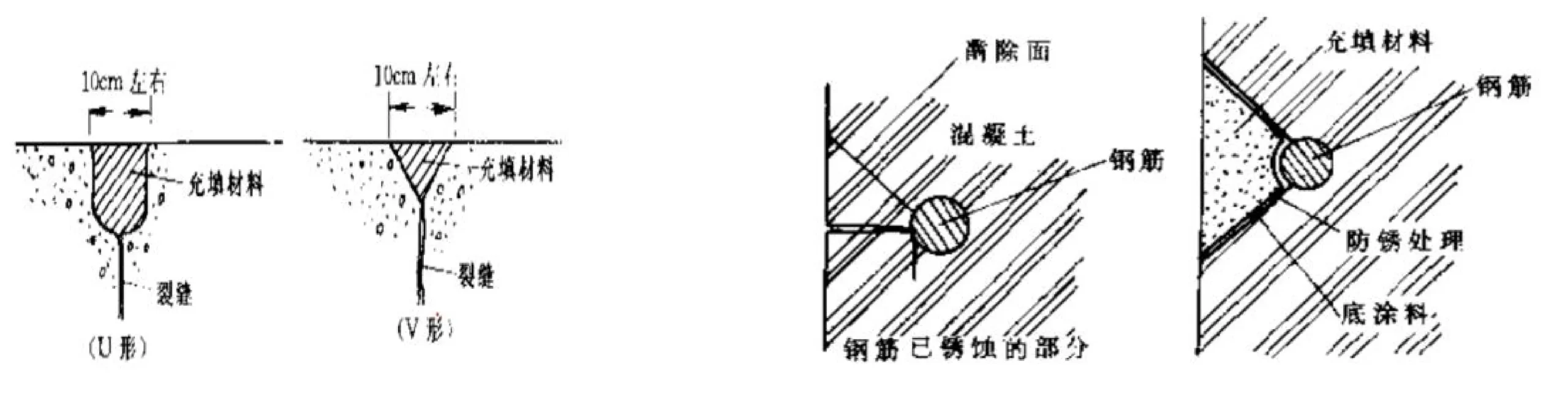
Chisel a U-shaped or V-shaped groove along the crack, approximately 10cm wide at the top, and then fill the groove with sealant.
Sealing materials include: cement mortar, epoxy mortar, elastic epoxy mortar, polymer cement mortar, etc.
For steel reinforcement corrosion: remove rust from the steel reinforcement, perform rust prevention treatment, and then fill the crack.
Epoxy grouting can be used to seal leaks according to customer requirements.
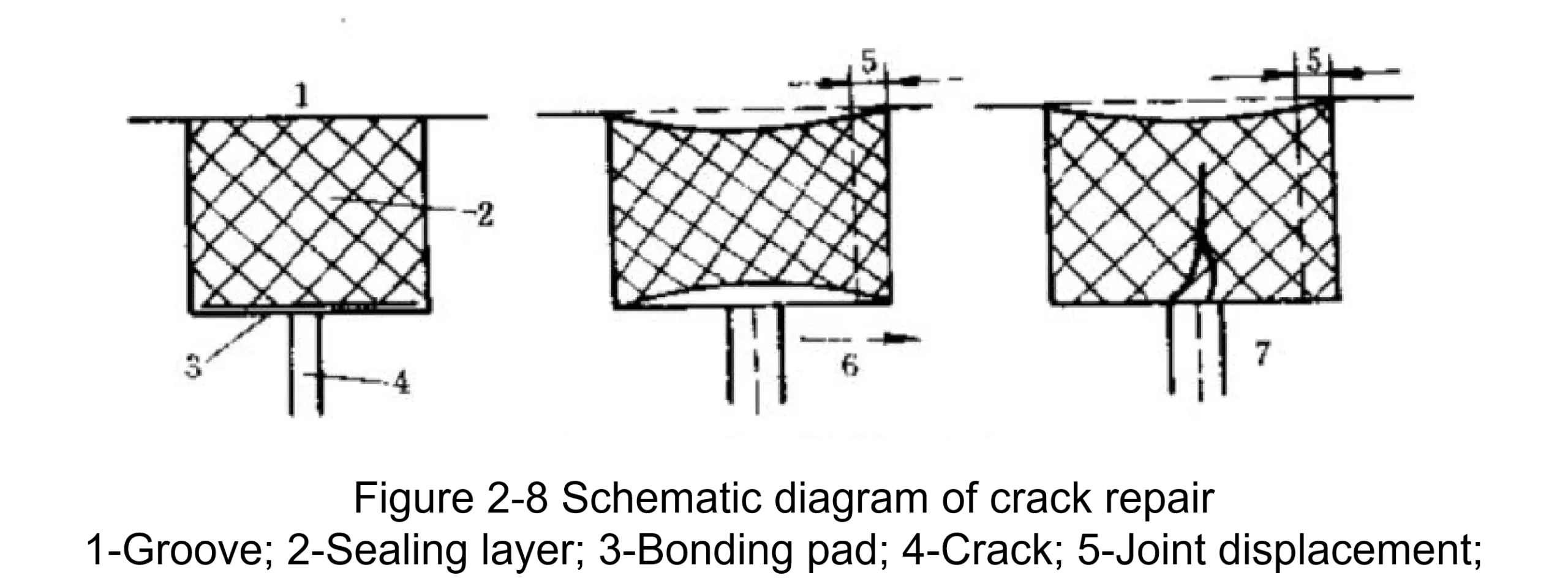
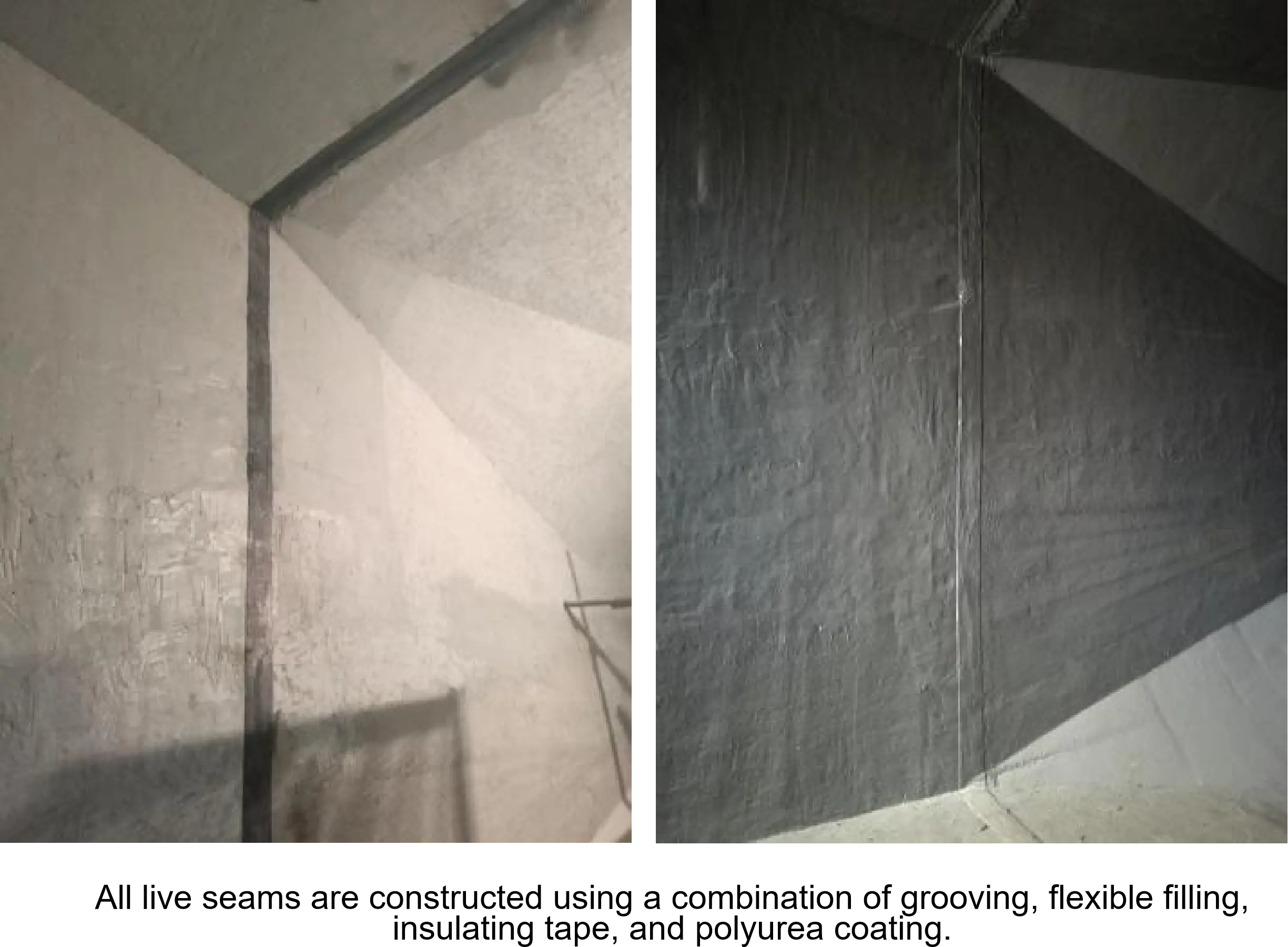
For a live joint, a U-shaped groove is cut along the crack's direction. A layer of non-adhesive material is placed at the bottom of the groove, followed by filling with an elastic sealant that adheres to both sides of the groove. This allows the sealant to deform freely along the entire width of the groove, preventing tearing forces from pulling the sealant apart when the crack deforms.
Epoxy grouting is used for leak sealing according to customer requirements.
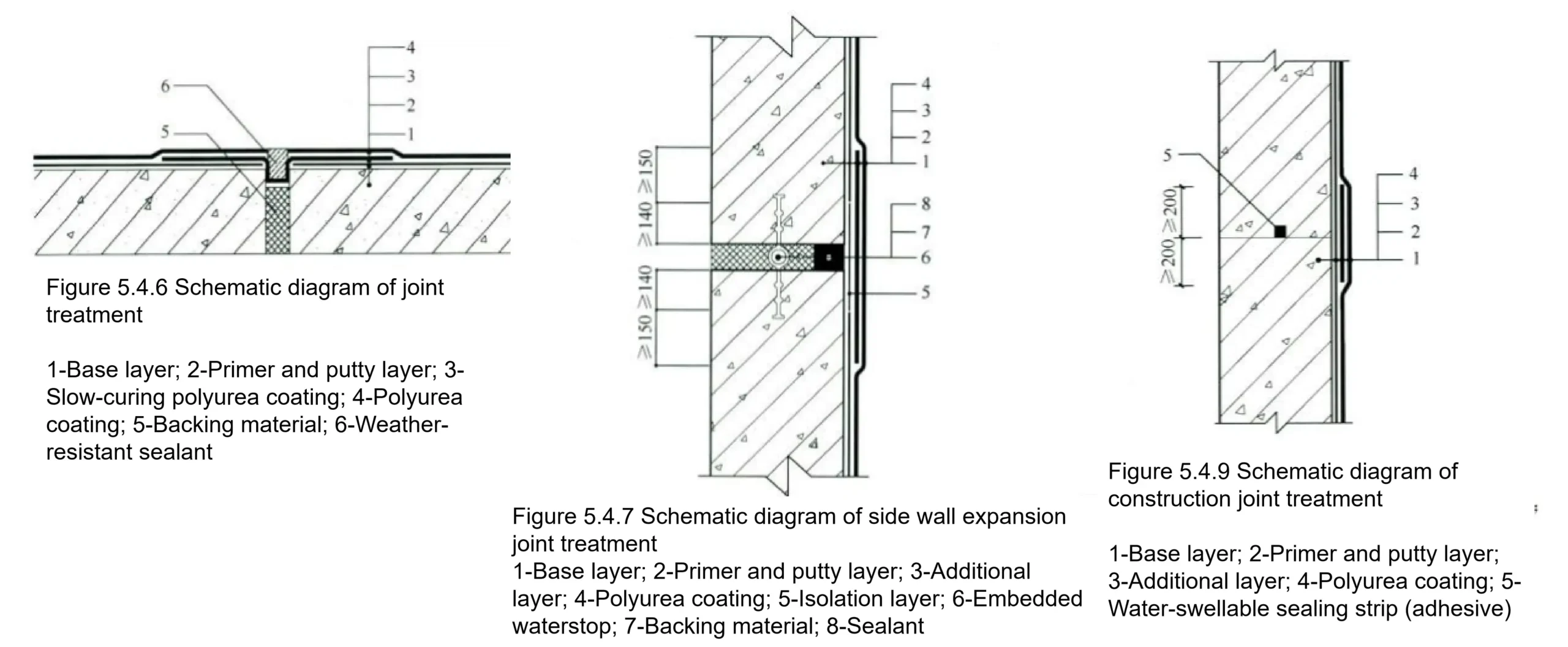
Isolation tape: butyl tape
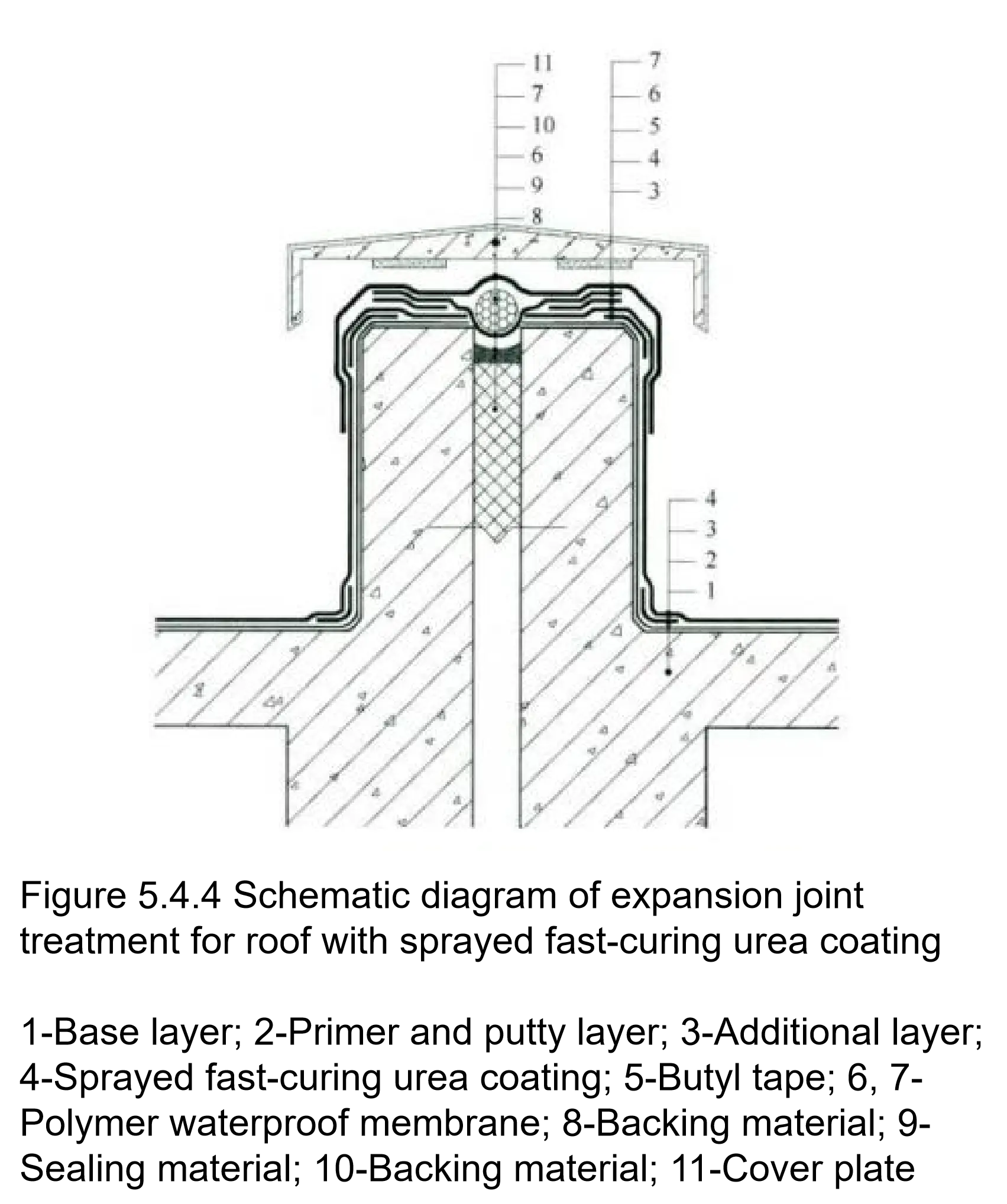

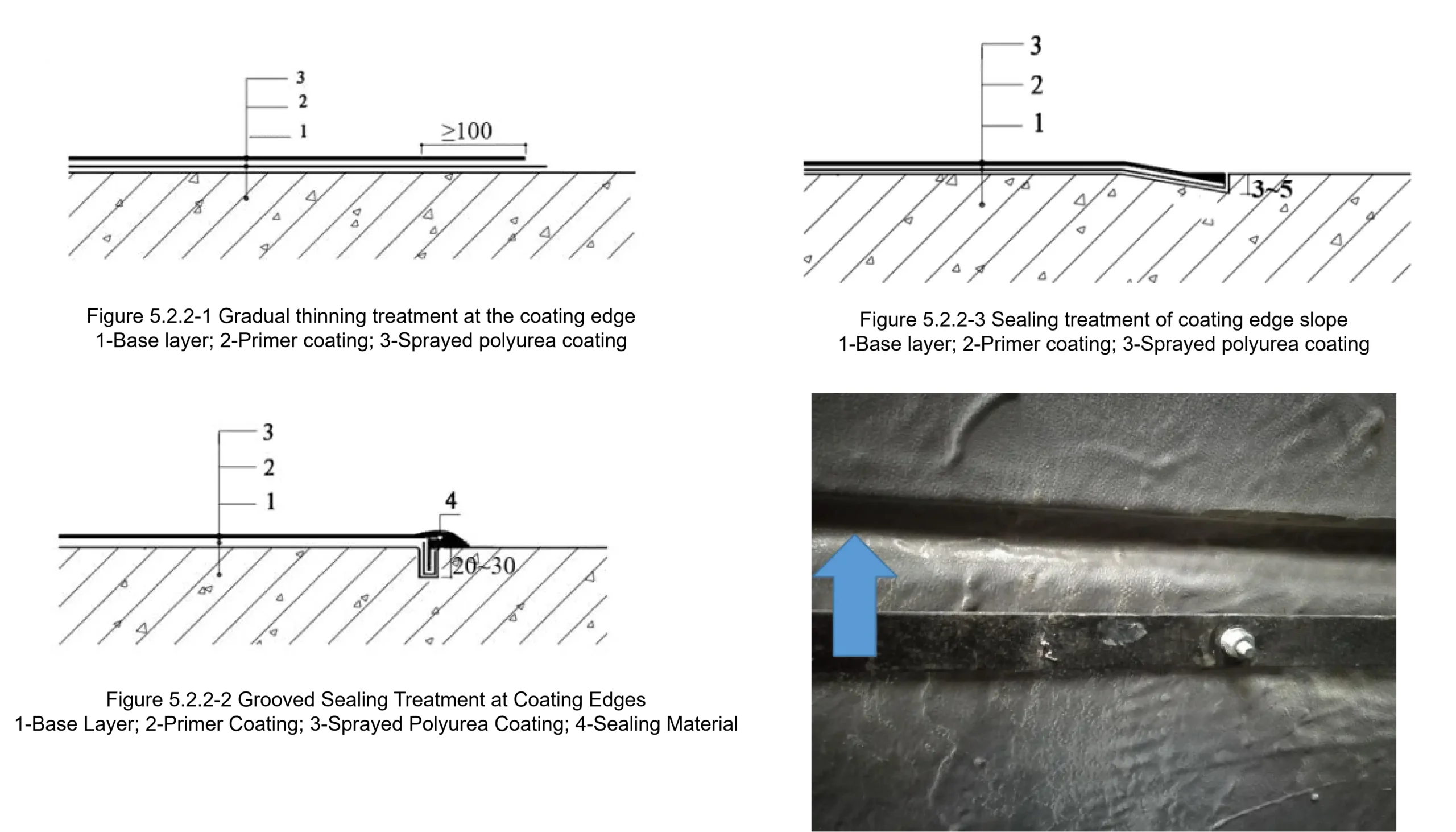
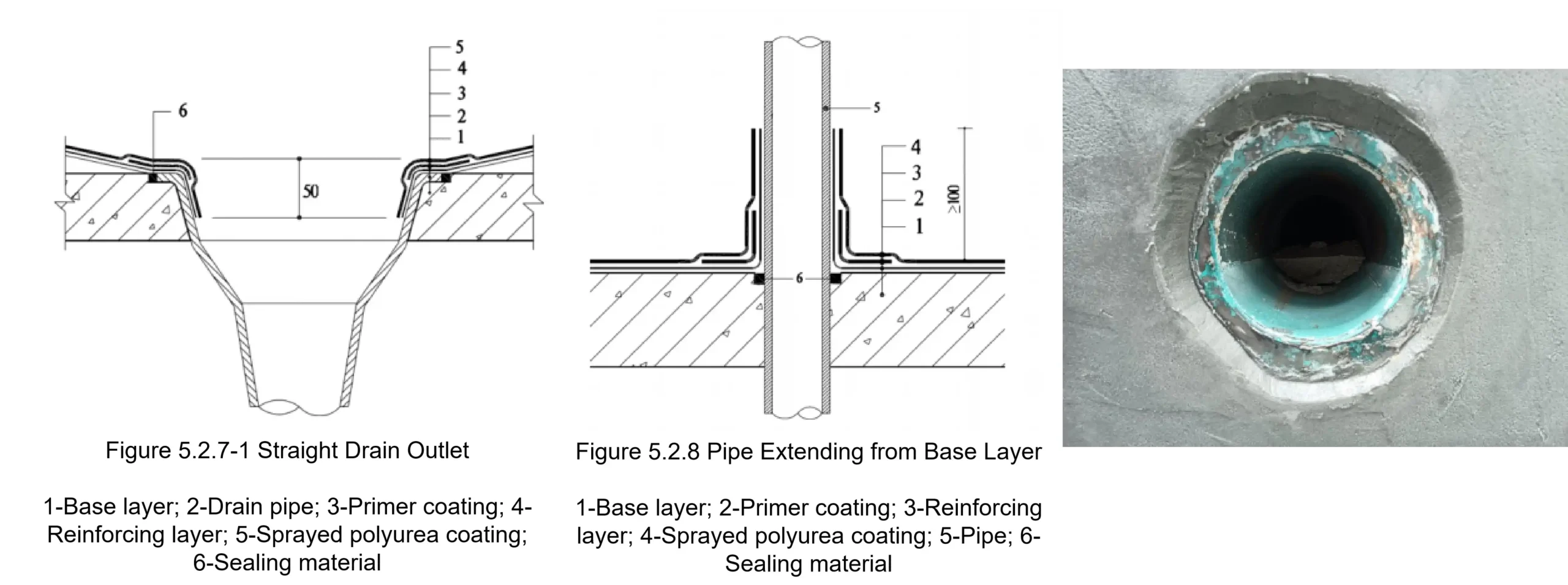





| Table 7.1.3 Sampling and Re-inspection Items for Incoming Materials | ||||
| Serial Number | Material Name | Sampling Batch | Sampling Quantity | Inspection Items |
| 1 | Sprayed rapid-set urea coating | Each 15 tons constitute one batch. If the quantity is less than 15 tons, it should also be counted as one batch. | Total weight according to formula: 40kg | Solid content, tensile strength, elongation at break, impermeability |
| 2 | Single-component slow-curing polyurea coating | 5kg | Solid content, surface drying time, complete drying time, tensile strength, elongation at break, impermeability, thick coating blistering, bond strength under standard test conditions | |
| 3 | Two-component slow-curing polyurea coating | Total weight according to formula: 5kg | Solid content, surface drying time, tensile strength, elongation at break, impermeability, bond strength under standard test conditions | |
| 4 | Base coat and putty | Count 5 tons as one batch. Any quantity less than 5 tons should also be counted as one batch. | Total weight according to formula: 1kg | Surface drying time, bond strength on dry substrate, peel strength on dry substrate |
| 5 | Coating with weather-resistant waterproofing paint | It should be counted as one batch for every 10 tons. If the quantity is less than 10 tons, it should also be regarded as one batch. | 2 kg | Solid content, bond strength, impermeability |
| 6 | Polyurethane building sealant | Count 5 tons as one batch. Any quantity less than 5 tons should also be counted as one batch. | 1. Single component: 6 vials; 2. Two-component: Total weight according to formula: 4kg | Leveling properties, surface drying time, adhesion at constant elongation, adhesion at constant elongation after immersion in water |
| 7 | Tissue matrix reinforcing material | Count by 5,000 square meters as one batch. If the area is less than 5,000 square meters, it should also be counted as one batch. | 2㎡ | Mass per unit area |
| Table 7.3.1 Quality Requirements for the Base Layer | |||
| Item | Quality Requirements | Testing Frequency | Testing Methods |
| Adhesion strength between the repaired area and the substrate (MPa) | ≥2.0 or damaged concrete substrate | Each 500㎡ should constitute one inspection batch, and each inspection batch should include at least 3 testing sites. | Current Industry Standard: Technical Specification for On-site Testing of Building Waterproofing Engineering (JGJ/T 299) Test for Tensile Bond Strength of Substrate Surface |
| Primer | Even application, normal curing, no missed areas, no buildup | Visual Inspection | |
7.3.2 After the surface treatment at the base layer is completed, it should be clean without any defects such as holes, hollowing, looseness, cracks, dust, oil stains, or foreign objects.
Testing method: Observation and inspection, as well as review of the acceptance records for concealed works.
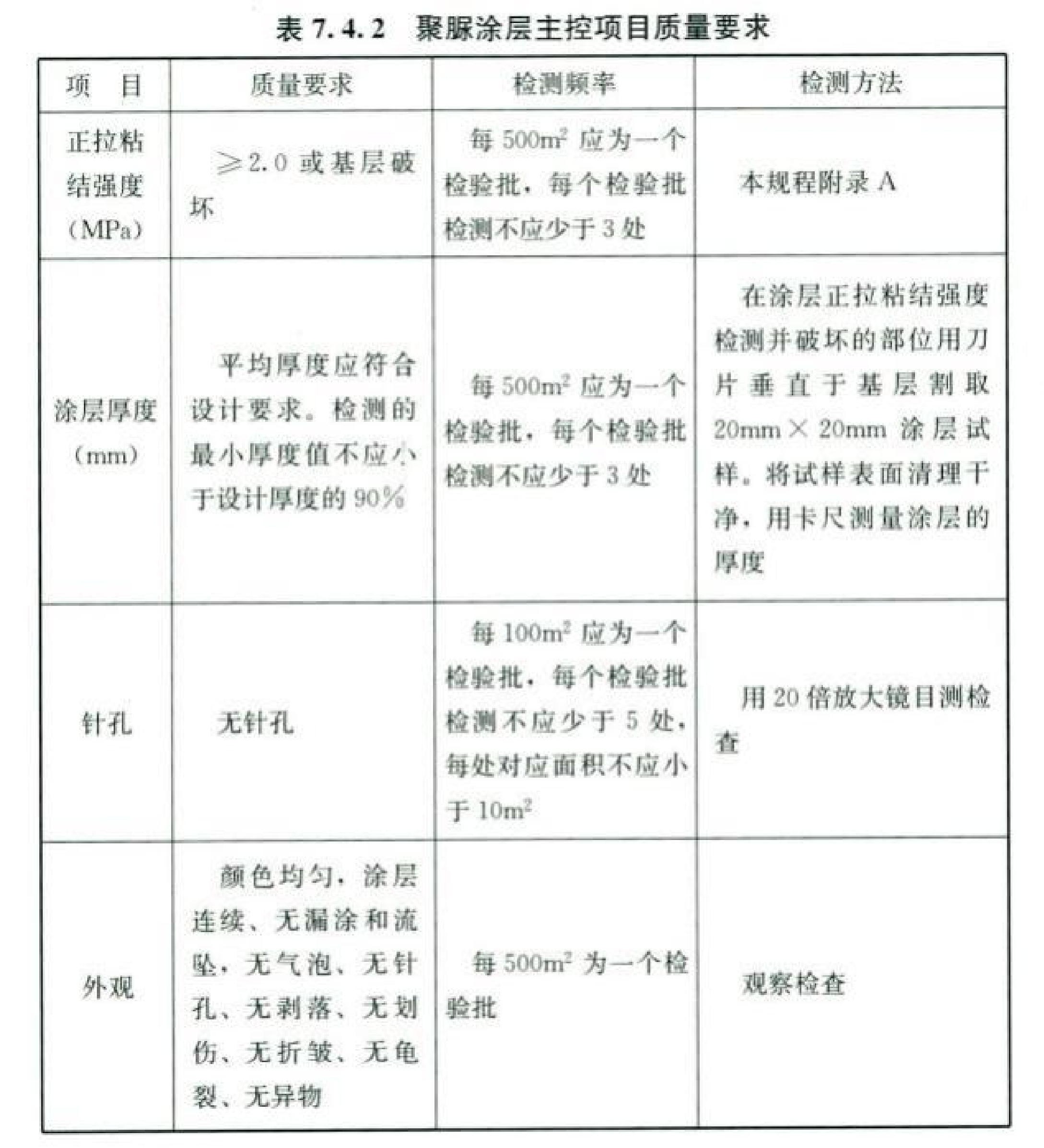
7.4.3 Underground waterproofing projects using polyurea coatings should be inspected and accepted in accordance with the waterproofing grade standards specified in the design documents. Other waterproofing and protection projects must not have any leakage.
Testing method: Observation after rain or water immersion for 2 hours, and water retention test for 24 hours.

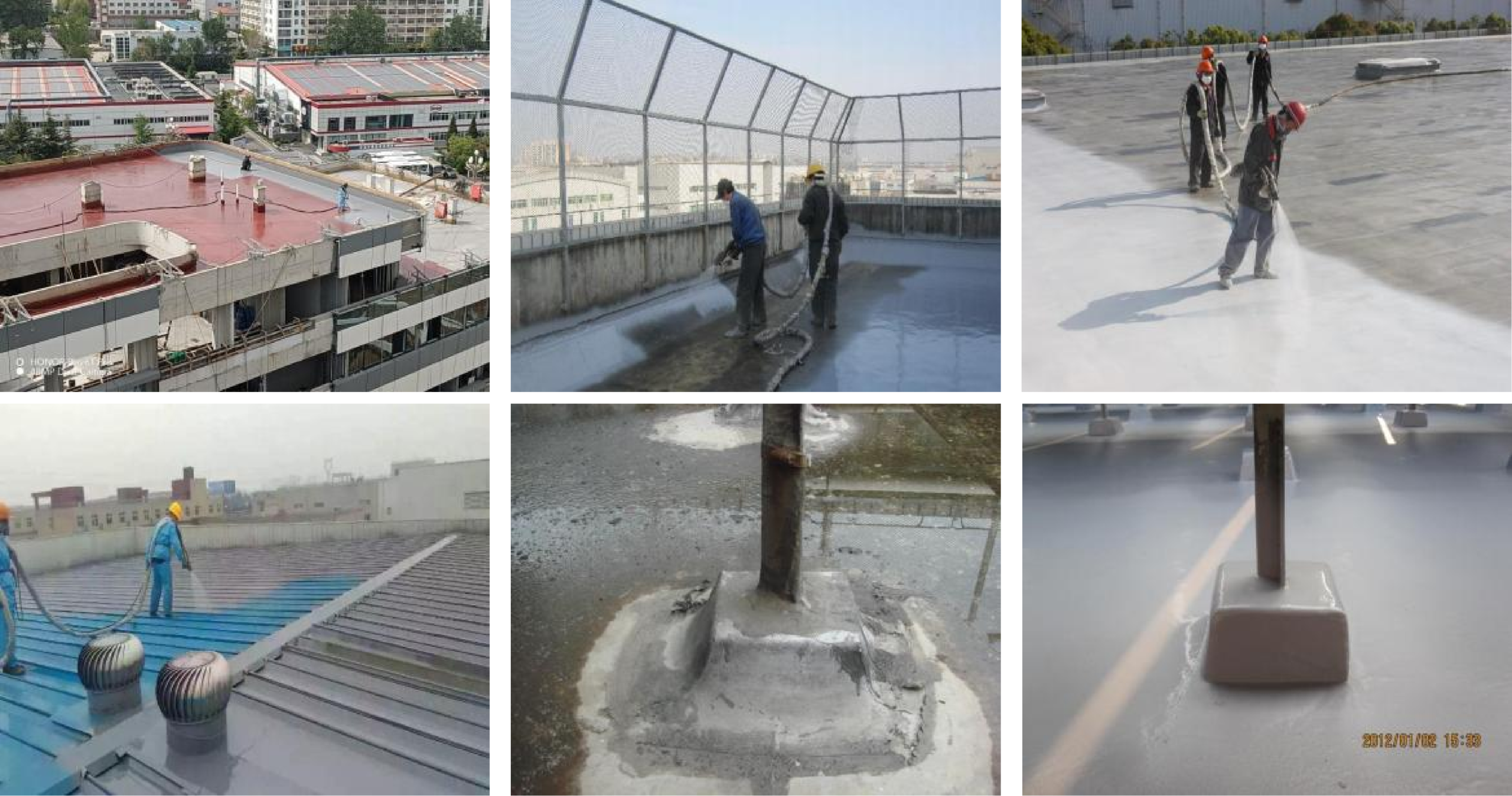
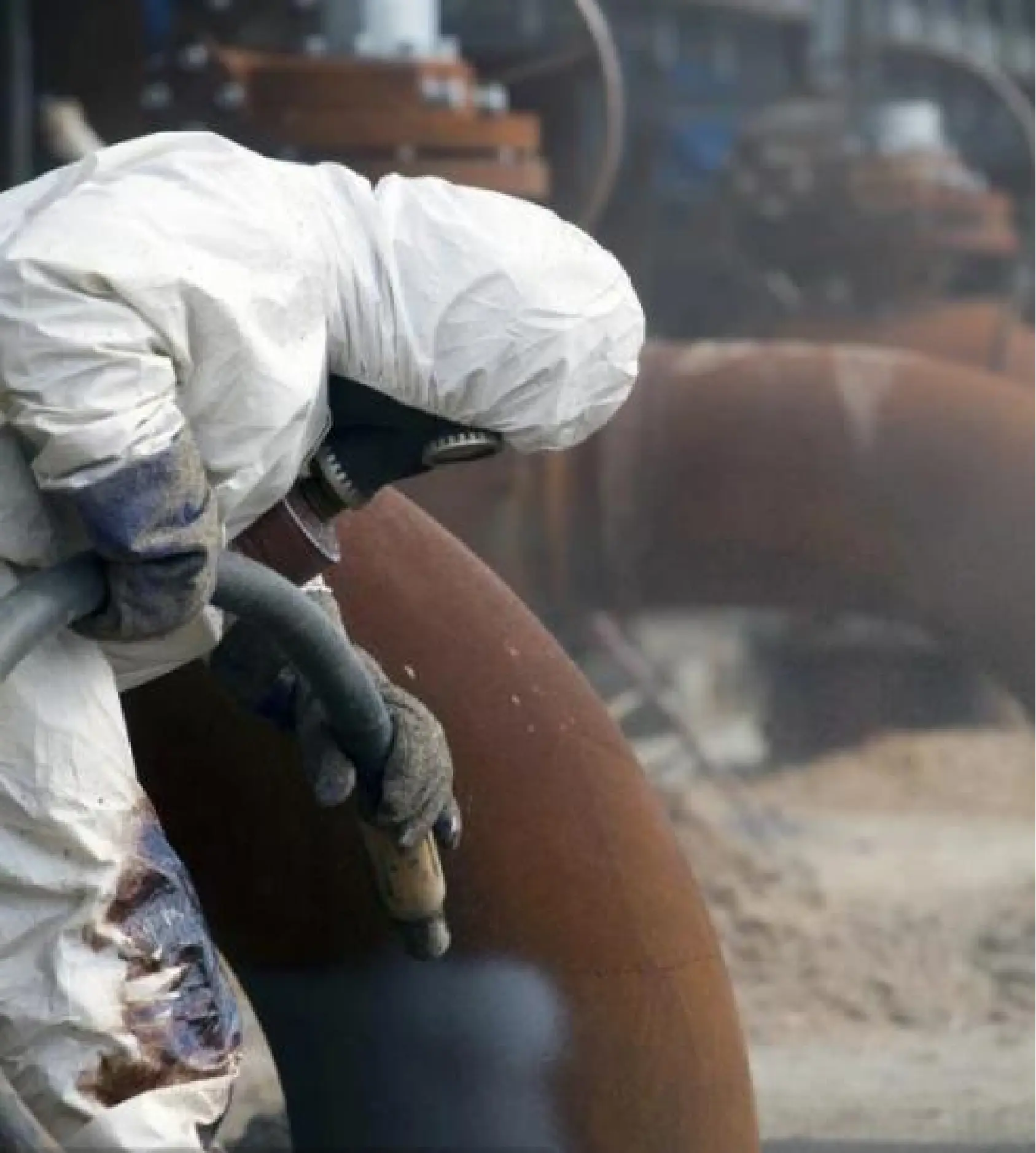
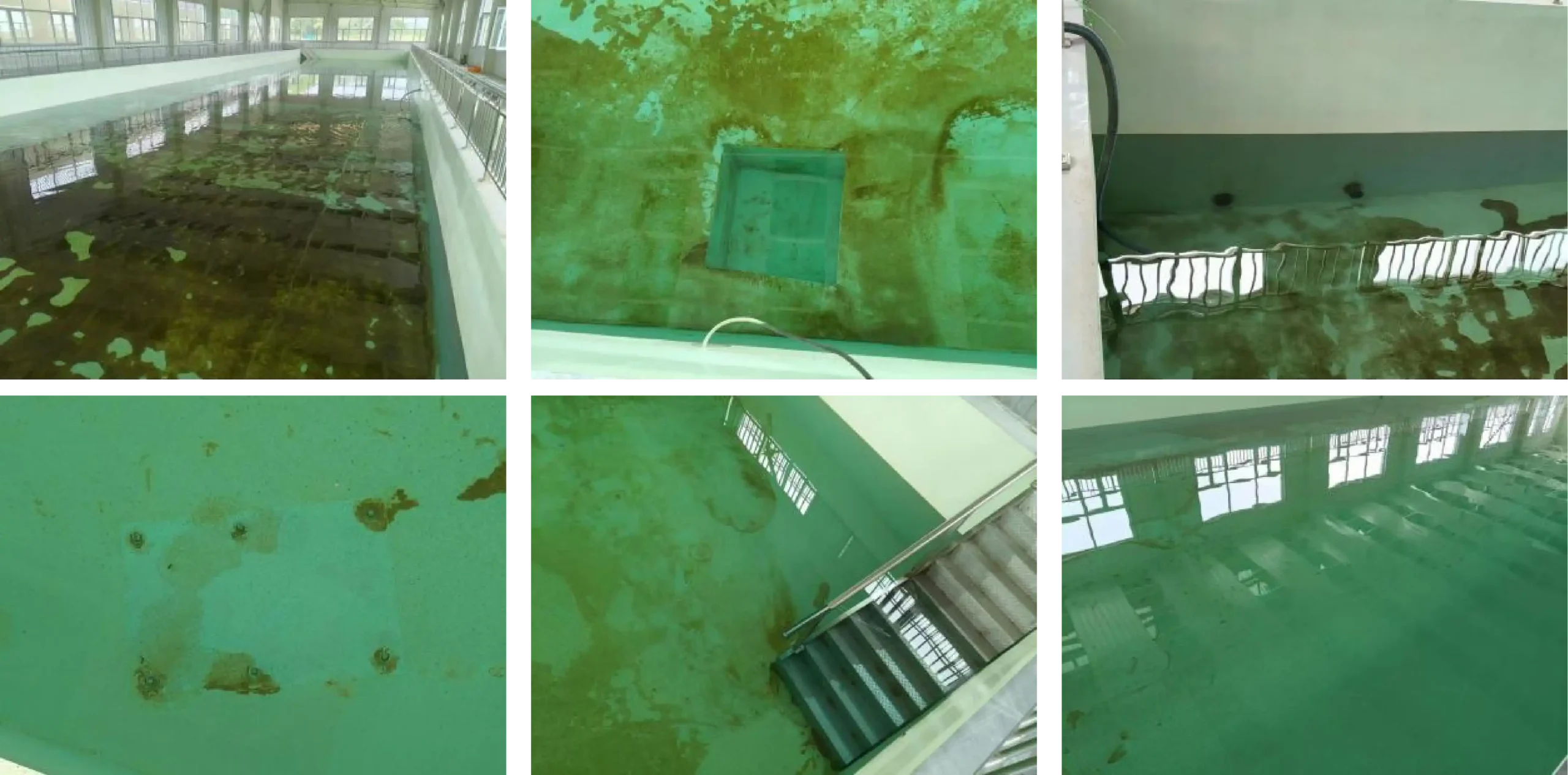
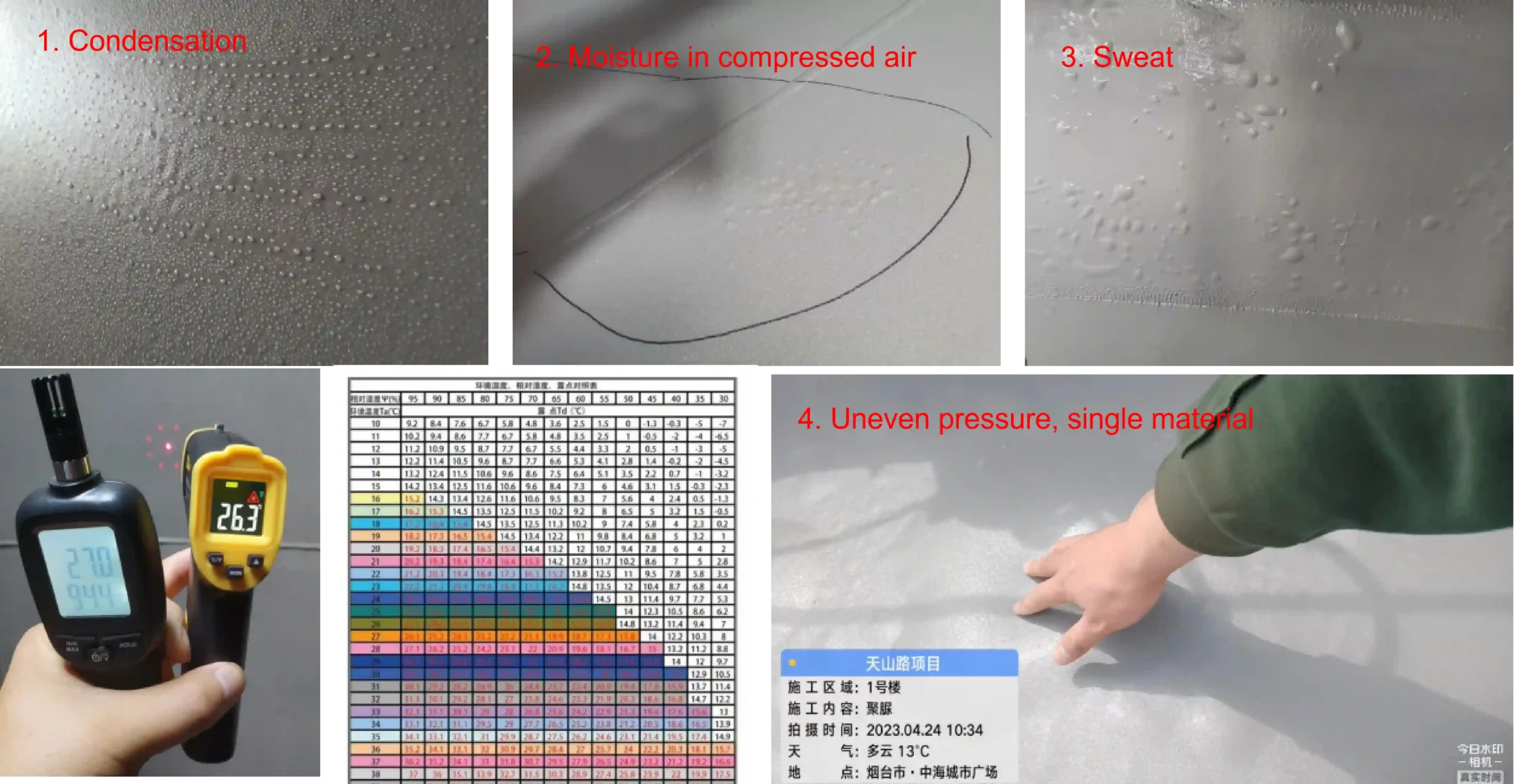
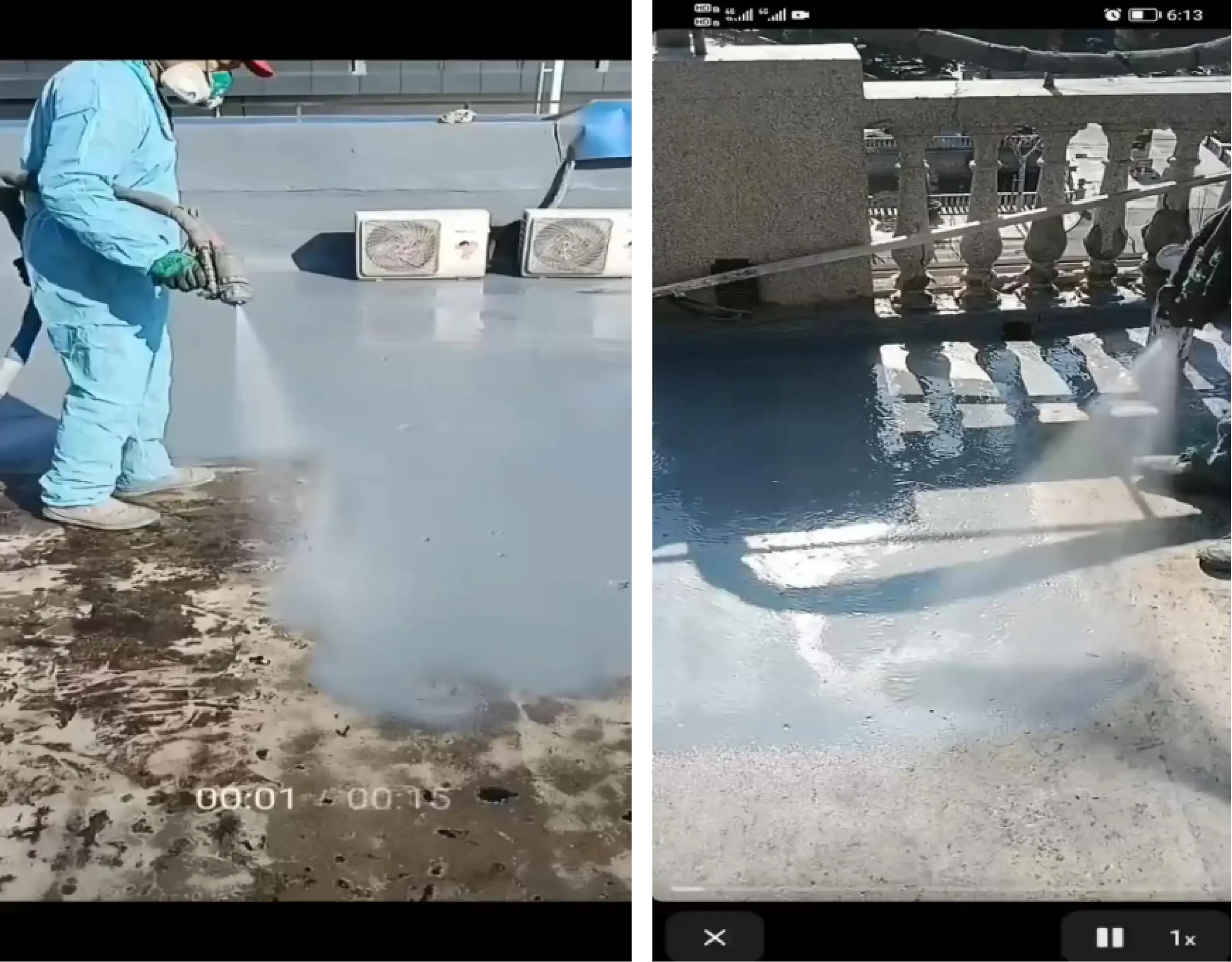
What are the problems in the spraying process shown in the video?
Issues:
1. Upwind spraying - - - Particulate matter pollution on the primer;
2. The distance between the spray gun and the base layer is too far - - - 0.5 meters;
3. Inclined spraying - - - Vertical spraying;
4. Unidirectional spraying - - - Crossed horizontally and vertically;
5. Coating lap risk - - - Spray in sequence.

Reason:
One-way spraying, with poor horizontal and vertical coverage;
2. The environment is dirty, with debris on the floor.
Reason:
The details were not handled properly.
Reason:
The base concrete was not stable and cracks appeared.
2. The gap was not dealt with.
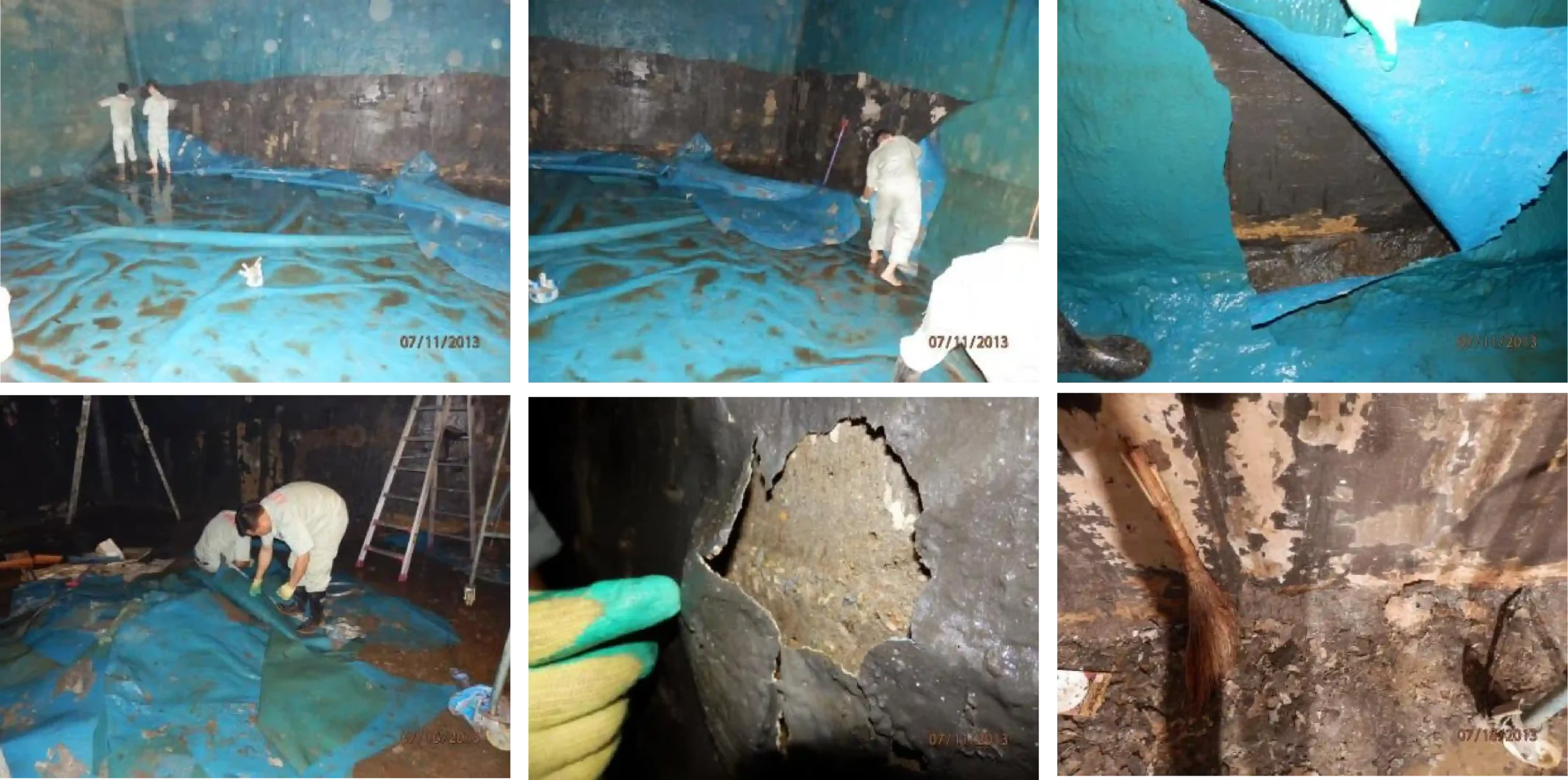
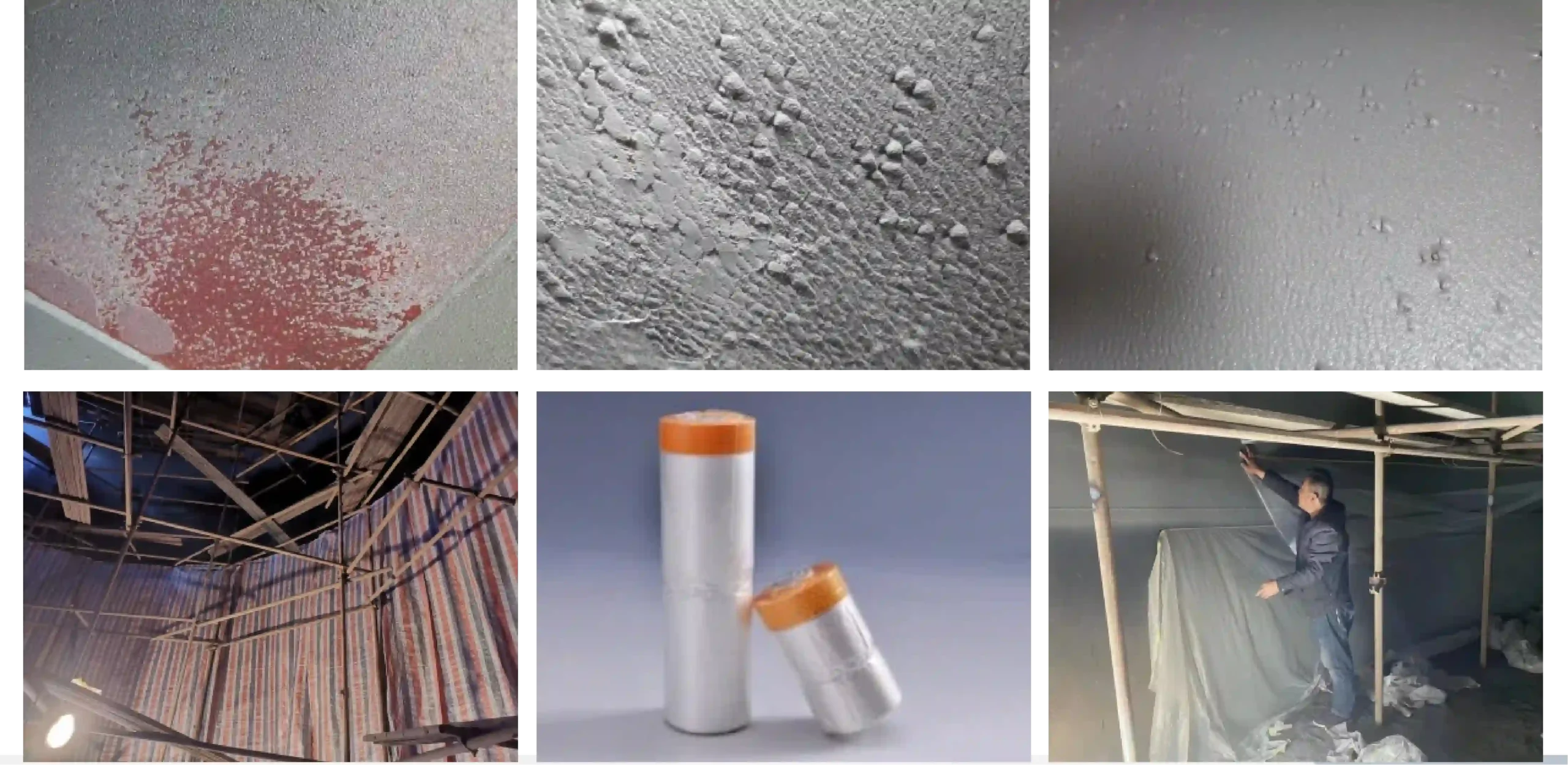
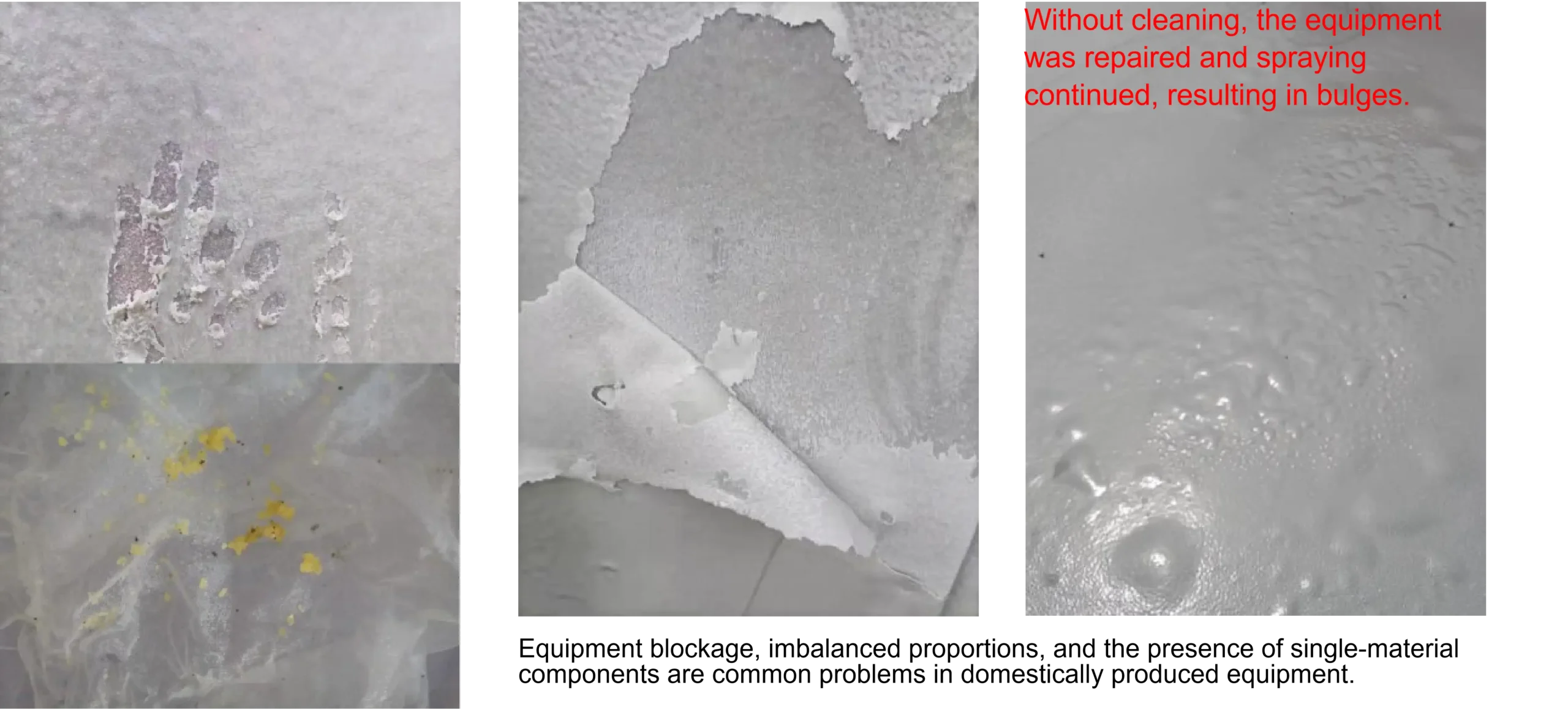






This is the reason why it is cheap.


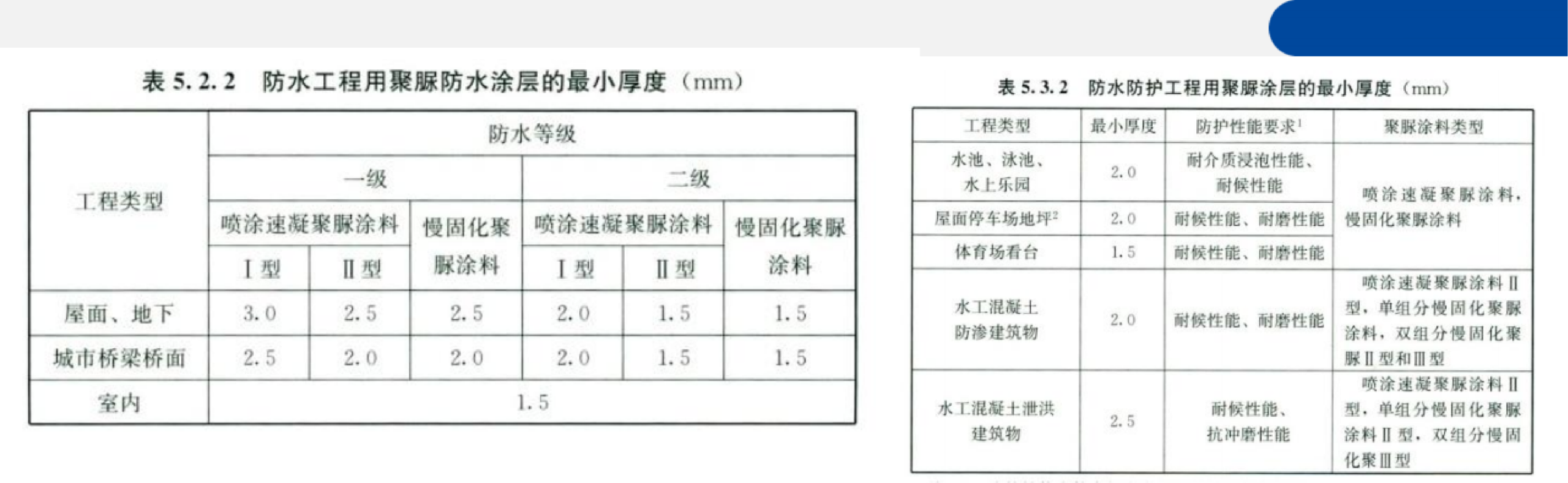
Common thicknesses: 1.5mm, 2.0mm
Wear resistance thickness: 3 - 5mm
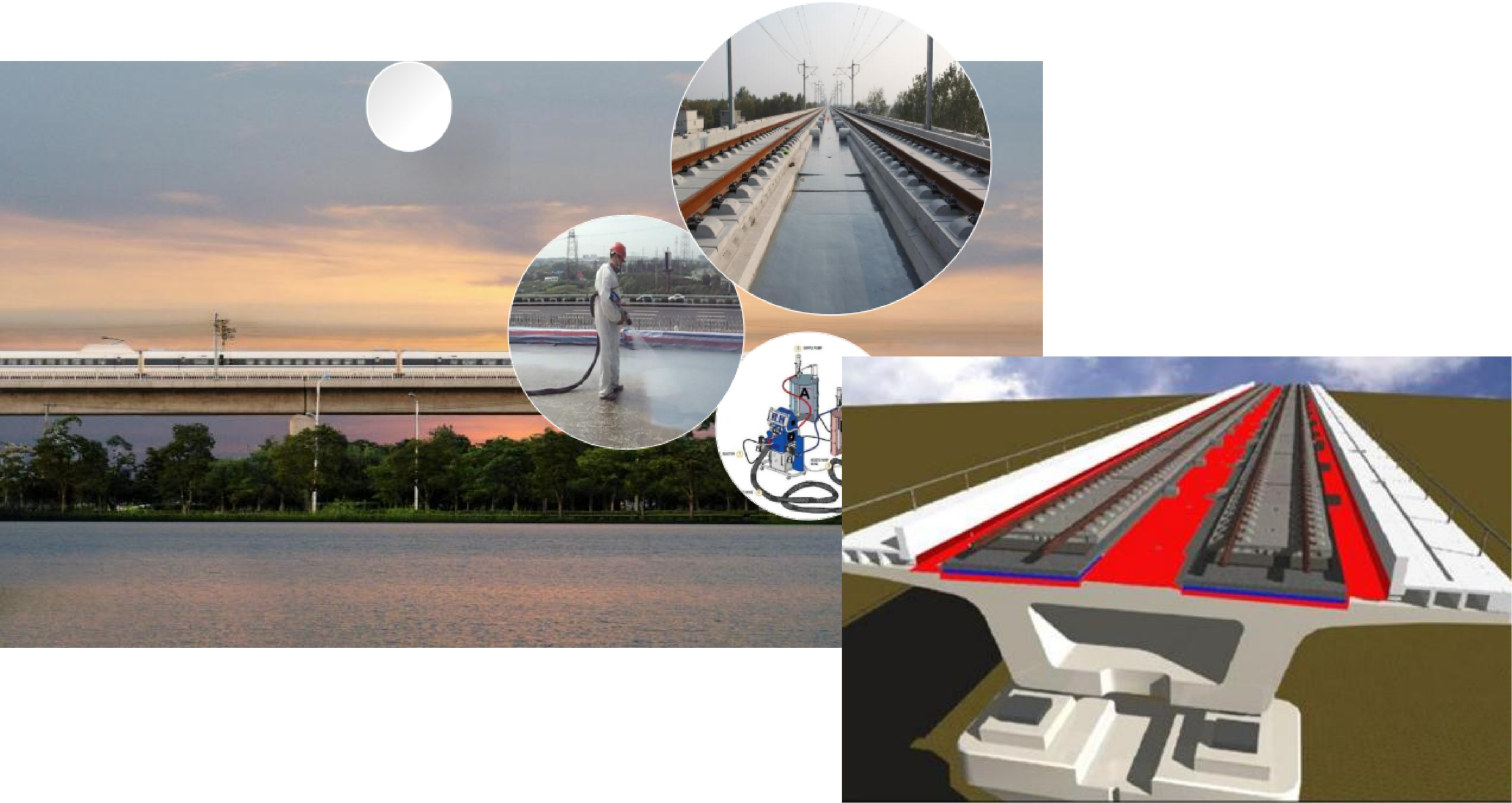
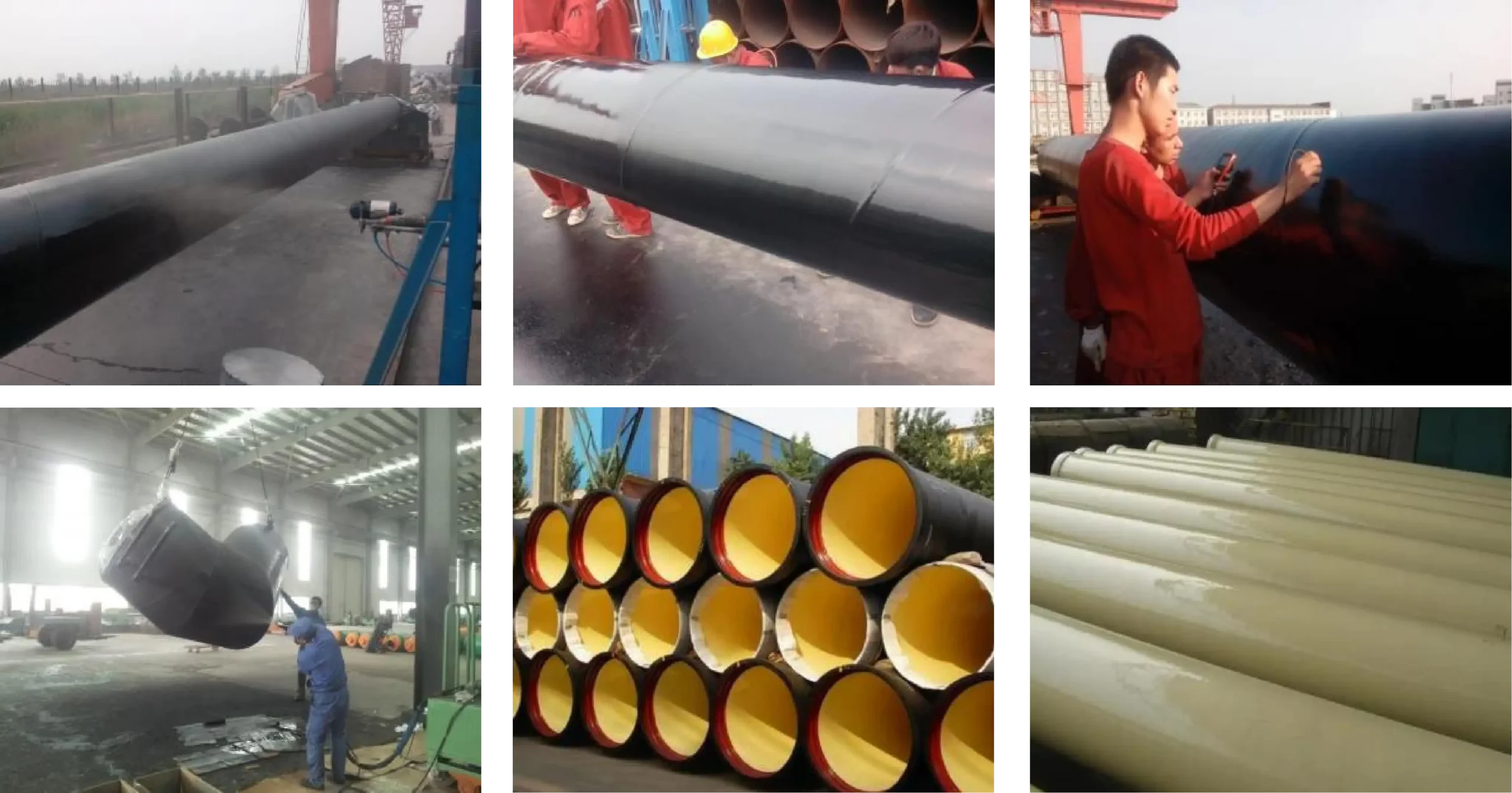
"Spraying polyurea" is never just referring to several materials or a few formulas; rather, it is an integrated application technology that combines materials, equipment, processes, and construction methods.
Discarding the aspects of equipment, process and construction and merely focusing on the polyurethane material is a manifestation of irresponsibility.

